
Bloc Suite is a comprehensive package that extends the functionality of the Flutter Bloc library. It provides additional utilities, widgets, and patterns to simplify state management in Flutter applications.
Features
- BlocWidget: A base widget that simplifies building UI components that depend on a BLoC.
- BlocSelectorWidget: A specialized widget that optimizes rebuilds by selecting specific parts of a Bloc's state.
- LifecycleBloc: A specialized Bloc that automatically handles lifecycle callbacks for events.
- FlutterBlocObserver: A BlocObserver that provides detailed logging capabilities for Flutter Bloc events and state changes.
- BlocEventTransformers: A collection of event transformers for handling event streams.
- ReplayBloc: A specialized Bloc which supports
undoandredooperations.
BlocWidget
The BlocWidget is a base widget that simplifies building UI components that depend on a BLoC. It handles the complexity of BLoC subscription and state management internally.
Example
class CounterBloc extends Cubit<int> {
CounterBloc() : super(0);
void increment() => emit(state + 1);
}
class CounterWidget extends BlocWidget<CounterBloc, int> {
const CounterWidget({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context, CounterBloc bloc, int state) {
return ...your_code;
}
}
BlocSelectorWidget
The BlocSelectorWidget is a specialized widget that optimizes rebuilds by selecting specific parts of a Bloc's state.
Example
class CounterState {
final int counterValue;
CounterState(this.counterValue);
}
class CounterBloc extends Cubit<CounterState> {
CounterBloc() : super(CounterState(0));
void increment() => emit(CounterState(state.counterValue + 1));
}
class CounterScreen extends BlocSelectorWidget<CounterBloc, CounterState, int> {
CounterScreen() : super(
bloc: CounterBloc(),
selector: (state) => state.counterValue,
);
@override
Widget build(context, bloc, value) {
return ...your_code;
}
}
LifecycleBloc
The LifecycleBloc is a specialized Bloc that automatically handles lifecycle callbacks for events.
Example
class CounterState {
final int value;
const CounterState(this.value);
}
sealed class CounterEvent extends LifecycleEvent {
const CounterEvent({super.onCompleted,super.onSuccess, super.onError});
}
class Increment extends CounterEvent {
const Increment({ super.onCompleted, super.onSuccess, super.onError});
}
class CounterBloc extends LifecycleBloc<CounterEvent, CounterState> {
CounterBloc() : super(CounterState(0)) {
on<Increment>(
(event, emit) => emit(CounterState(state.value + 1)),
// optional
transformer: BlocEventTransformer.throttle(
const Duration(milliseconds: 500),
),
);
}
}
class CounterScreen extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final bloc = context.read<CounterBloc>();
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: BlocBuilder<CounterBloc, CounterState>(
builder: (context, state) {
return Text('Count: ${state.value}');
},
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () => bloc.add(
Increment(
onSuccess: () => print('Counter increased'),
onCompleted: () => print('Operation completed'),
onError: (error) => print('Error: $error'),
),
),
child: Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
BlocEventTransformer
The BlocEventTransformer class provides a collection of event transformers that help control the flow of events in BLoC (Business Logic Component) patterns. These transformers allow you to manipulate events before they are processed by the BLoC's event handlers.
Choosing the Right Transformer
| Transformer | Sequential | Distinct | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
delay |
✅ Always | 🔄 Configurable | Postpone processing (e.g., brief loading indicators). |
debounce |
✅ Always | 🔄 Configurable | Wait for inactivity before processing (e.g., search inputs, form validation). |
throttle |
✅ Always | 🔄 Configurable | Control frequent events (e.g., scrolling, resizing). |
restartable |
✅ Always | 🔄 Configurable | Cancel outdated events when new ones arrive (e.g., live search API calls). |
sequential |
✅ Always | 🔄 Configurable | Ensure ordered execution (e.g., sending messages one by one). |
droppable |
✅ Always | 🔄 Configurable | Process only the latest event, dropping older ones (e.g., UI animations). |
skip |
🔄 Configurable | 🔄 Configurable | Ignore initial events (e.g., first trigger in a lifecycle). |
distinct |
🔄 Configurable | ✅ Always | Avoid duplicate event processing (e.g., filtering unchanged user actions). |
take |
🔄 Configurable | 🔄 Configurable | Limit the number of events (e.g., first N items in a list). |
1. delay
Delays the processing of each event by a specified duration, shifting the entire sequence forward in time.
Parameters:
duration: The time to delay each event.distinct: When true, skips events that are equal to the previous event. Default:false
Usage:
on<ExampleEvent>(
_handleEvent,
transformer: BlocEventTransformer.delay(const Duration(seconds: 1)),
);
Visual Representation:
Input: --a--------b---c--->
Output: ----a--------b---c-> (with 1s delay)
2. debounce
Debouncing is useful when the event is frequently being triggered in a short interval of time Useful for handling rapidly firing events like search input.
Parameters:
duration: The time window to wait for inactivity.
Usage:
on<SearchQueryEvent>(
_handleSearchQuery,
transformer: BlocEventTransformer.debounce(const Duration(milliseconds: 300)),
);
Visual Representation:
Input: --a-ab-bc--c------d->
Output: --------c---------d-> (with 300ms debounce)
3. throttle
Limits how often an event can be processed.
Parameters:
duration: The minimum time between processed events.leading: Iftrue, process the first event in a burst (default:true).trailing: Iftrue, process the last event in a burst (default:false).
Usage:
on<ScrollEvent>(
_handleScrollEvent,
transformer: BlocEventTransformer.throttle(
const Duration(milliseconds: 200),
trailing: true,
),
);
Visual Representation:
Input: --a-ab-bc--c-------d-->
Output: --a----b----c-------d-> (with 200ms throttle, leading: true)
4. restartable
Cancels any in-progress event processing when a new event arrives. Useful for operations that can be abandoned if newer data is available.
Usage:
on<FetchDataEvent>(
_handleFetchData,
transformer: BlocEventTransformer.restartable(),
);
Visual Representation:
Input: --a-----b---c--->
Processing: --[a]--X
--[b]X
--[c]--->
Output: ---------x----x--->
5. sequential
Processes events one after another, ensuring order is maintained. Events are queued and handled in sequence.
Usage:
on<SaveDataEvent>(
_handleSaveData,
transformer: BlocEventTransformer.sequential(),
);
Visual Representation:
Input: --a--b--c-------->
Processing: --[a]--[b]--[c]-->
Output: ----x----x----x-->
6. droppable
Ignores new events until the current event processing is complete.
Usage:
on<ProcessIntensiveEvent>(
_handleIntensiveTask,
transformer: BlocEventTransformer.droppable(),
);
Visual Representation:
Input: --a--b--c-------->
Processing: ---[a]-------->
Output: --------x---------> (b and c are dropped)
7. skip
Skips a specified number of initial events.
Parameters:
count: The number of events to skip.
Usage:
on<PageLoadEvent>(
_handlePageLoad,
transformer: BlocEventTransformer.skip(1), // Skip first event
);
Visual Representation:
Input: --a--b--c--d--e-->
Output: -----b--c--d--e--> (with count: 1)
7. distinct
Skips events if they are equal to the previous event.
Usage:
on<FilterEvent>(
_handleFilterEvent,
transformer: BlocEventTransformer.distinct(),
);
Visual Representation:
Input: --a--a--b--b--c--c-->
Output: --a-----b-----c-----> (duplicate events are skipped)
8. take
Creates an event transformer that takes a specified number of events.
Usage:
on<LoadEvent>(
_handleLoadEvent,
transformer: BlocEventTransformer.take(3), // Take first 3 events
);
Visual Representation:
Input: --a--b--c--d--e-->
Output: --a--b--c--------> (with limit: 3)
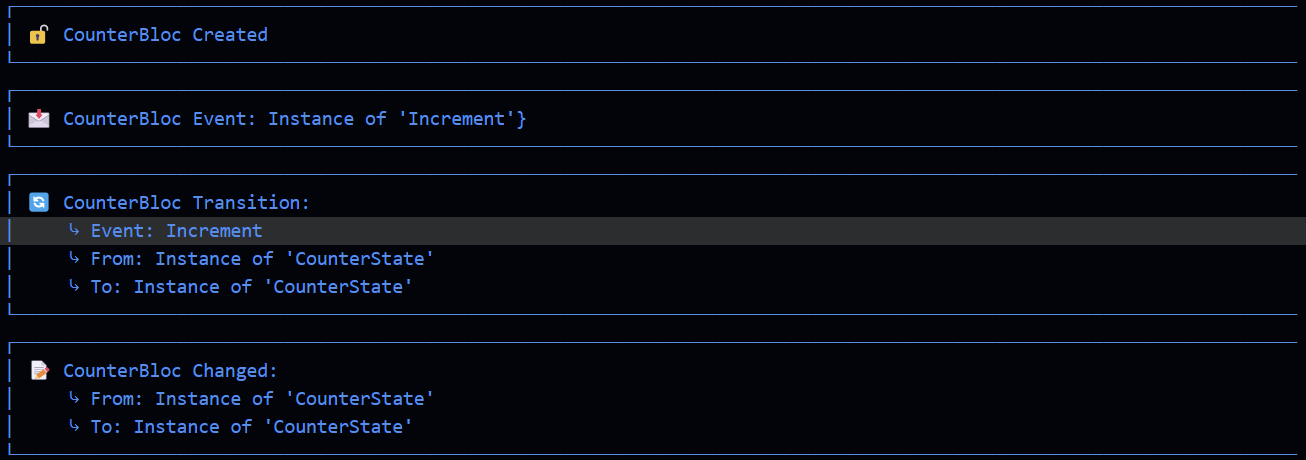
FlutterBlocObserver
The FlutterBlocObserver is a BlocObserver that provides detailed logging capabilities for Flutter Bloc events and state changes.
Example
void main() {
Bloc.observer = FlutterBlocObserver(
enabled: true,
printEvents: true,
printTransitions: true,
printChanges: true,
printCreations: true,
printClosings: true,
);
runApp(MyApp());
}
...more
ReplayBloc
This section is inspired by the replay_bloc package from the official Bloc library. For more detailed information and examples, please refer to the original repository.
Creating a ReplayCubit
class CounterCubit extends ReplayCubit<int> {
CounterCubit() : super(0);
void increment() => emit(state + 1);
}
Using a ReplayCubit
void main() {
final cubit = CounterCubit();
// trigger a state change
cubit.increment();
print(cubit.state); // 1
// undo the change
cubit.undo();
print(cubit.state); // 0
// redo the change
cubit.redo();
print(cubit.state); // 1
}
ReplayCubitMixin
If you wish to be able to use a ReplayCubit in conjuction with a different type of cubit like HydratedCubit, you can use the ReplayCubitMixin.
class CounterCubit extends HydratedCubit<int> with ReplayCubitMixin {
CounterCubit() : super(0);
void increment() => emit(state + 1);
void decrement() => emit(state - 1);
@override
int fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => json['value'] as int;
@override
Map<String, int> toJson(int state) => {'value': state};
}
Creating a ReplayBloc
class CounterEvent extends ReplayEvent {}
class CounterIncrementPressed extends CounterEvent {}
class CounterDecrementPressed extends CounterEvent {}
class CounterBloc extends ReplayBloc<CounterEvent, int> {
CounterBloc() : super(0) {
on<CounterIncrementPressed>((event, emit) => emit(state + 1));
on<CounterDecrementPressed>((event, emit) => emit(state - 1));
}
}
Using a ReplayBloc
void main() {
// trigger a state change
final bloc = CounterBloc()..add(CounterIncrementPressed());
// wait for state to update
await bloc.stream.first;
print(bloc.state); // 1
// undo the change
bloc.undo();
print(bloc.state); // 0
// redo the change
bloc.redo();
print(bloc.state); // 1
}
ReplayBlocMixin
If you wish to be able to use a ReplayBloc in conjuction with a different type of cubit like HydratedBloc, you can use the ReplayBlocMixin.
sealed class CounterEvent with ReplayEvent {}
final class CounterIncrementPressed extends CounterEvent {}
final class CounterDecrementPressed extends CounterEvent {}
class CounterBloc extends HydratedBloc<CounterEvent, int> with ReplayBlocMixin {
CounterBloc() : super(0) {
on<CounterIncrementPressed>((event, emit) => emit(state + 1));
on<CounterDecrementPressed>((event, emit) => emit(state - 1));
}
@override
int fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => json['value'] as int;
@override
Map<String, int> toJson(int state) => {'value': state};
}
Contributing
Contributions are welcome! Please open an issue or submit a pull request on GitHub.
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License.




