connectivity_plus
This plugin allows Flutter apps to discover network connectivity types that can be used.
Note
You should not rely on the current connectivity status to decide whether you can reliably make a network request. Always guard your app code against timeouts and errors that might come from the network layer. Connection type availability does not guarantee that there is an Internet access. For example, the plugin might return Wi-Fi connection type, but it might be a connection with no Internet access due to network requirements (like on hotel Wi-Fi networks where user often needs to go through a captive portal to authorize first).
Platform Support
| Android | iOS | MacOS | Web | Linux | Windows |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
Requirements
- Flutter >=3.19.0
- Dart >=3.3.0 <4.0.0
- iOS >=12.0
- MacOS >=10.14
- Android
compileSDK34 - Java 17
- Android Gradle Plugin >=8.3.0
- Gradle wrapper >=8.4
Usage
Sample usage to check currently available connection types:
import 'package:connectivity_plus/connectivity_plus.dart';
final List<ConnectivityResult> connectivityResult = await (Connectivity().checkConnectivity());
// This condition is for demo purposes only to explain every connection type.
// Use conditions which work for your requirements.
if (connectivityResult.contains(ConnectivityResult.mobile)) {
// Mobile network available.
} else if (connectivityResult.contains(ConnectivityResult.wifi)) {
// Wi-fi is available.
// Note for Android:
// When both mobile and Wi-Fi are turned on system will return Wi-Fi only as active network type
} else if (connectivityResult.contains(ConnectivityResult.ethernet)) {
// Ethernet connection available.
} else if (connectivityResult.contains(ConnectivityResult.vpn)) {
// Vpn connection active.
// Note for iOS and macOS:
// There is no separate network interface type for [vpn].
// It returns [other] on any device (also simulator)
} else if (connectivityResult.contains(ConnectivityResult.bluetooth)) {
// Bluetooth connection available.
} else if (connectivityResult.contains(ConnectivityResult.other)) {
// Connected to a network which is not in the above mentioned networks.
} else if (connectivityResult.contains(ConnectivityResult.none)) {
// No available network types
}
You can also listen for active connectivity types changes by subscribing to the stream exposed by the plugin.
This method should ensure emitting only distinct values.
import 'package:connectivity_plus/connectivity_plus.dart';
@override
initState() {
super.initState();
StreamSubscription<List<ConnectivityResult>> subscription = Connectivity().onConnectivityChanged.listen((List<ConnectivityResult> result) {
// Received changes in available connectivity types!
});
}
// Be sure to cancel subscription after you are done
@override
dispose() {
subscription.cancel();
super.dispose();
}
Platform Support
The following table shows which ConnectivityResult values are supported per platform.
| Android | iOS | Web | MacOS | Windows | Linux | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wifi | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: |
| bluetooth | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | ||||
| ethernet | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | |
| mobile | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | |||
| vpn | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | |||
| other | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: |
none is supported on all platforms by default.
Android
Connectivity changes are no longer communicated to Android apps in the background starting with Android O (8.0). You should always check for connectivity status when your app is resumed. The broadcast is only useful when your application is in the foreground.
iOS & MacOS
On iOS simulators, the connectivity types stream might not update when Wi-Fi status changes. This is a known issue.
Starting with iOS 12 and MacOS 10.14, the implementation uses NWPathMonitor to obtain the enabled connectivity types. We noticed that this observer can give multiple or unreliable results. For example, reporting connectivity "none" followed by connectivity "wifi" right after reconnecting.
We recommend to use the onConnectivityChanged with this limitation in mind, as the method doesn't filter events, nor it ensures distinct values.
Web
In order to retrieve information about the quality/speed of a browser's connection, the web implementation of the connectivity plugin uses the browser's NetworkInformation Web API, which as of this writing (June 2020) is still "experimental", and not available in all browsers:
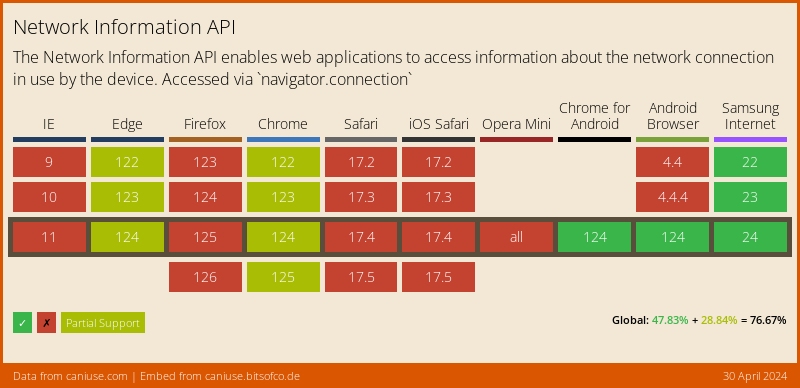
On desktop browsers, this API only returns a very broad set of connectivity statuses (One of 'slow-2g', '2g', '3g', or '4g'), and may not provide a Stream of changes. Firefox still hasn't enabled this feature by default.
Fallback to navigator.onLine
For those browsers where the NetworkInformation Web API is not available, the plugin falls back to the NavigatorOnLine Web API, which is more broadly supported:
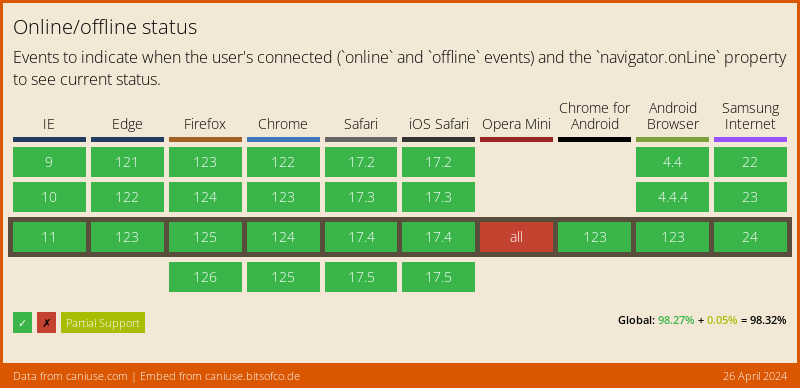
The NavigatorOnLine API is provided by dart:html, and only supports a boolean connectivity status (either online or offline), with no network speed information. In those cases the plugin will return either wifi (when the browser is online) or none (when it's not).
Other than the approximate "downlink" speed, where available, and due to security and privacy concerns, no Web browser will provide any specific information about the actual network your users' device is connected to, like the SSID on a Wi-Fi, or the MAC address of their device.


