Tarsier ENV
Documentation • Issues • Example • License • Pub.dev
A Dart/Flutter package for creating/loading .env files and generating a Dart file containing environment variables with static getters. This package simplifies the management of environment variables and helps automate the process of accessing them within your project.
This package is a little bit similar to flutter_dotenv, but with enhanced functionality, including static variable name access and dynamic value resolution.
✨ Features
- Creates
.envfile if not existed with pre-defined keys and values. - Loads
.envfiles and parses them into aMap<String, String>. - Generates a
env.dartfile with static getters for each environment variable. - Automatically inserts the import statement and
Env.init()initialization inmain.dart. - Supports custom paths for the
env.dartfile.
🚀 Installation
Add Dependency
Add the following to your pubspec.yaml file:
dependencies:
tarsier_env: ^1.0.6
Then run this command:
flutter pub get
🖥️ Commands
The dart run tarsier_env <parameters> <options> syntax maps directly with required parameters (generate, new). Options is when you use command generate for custom path.
dart run tarsier_env new
dart run tarsier_env generate
dart run tarsier_env generate custom_path_for_env/subpath
📒 Usage Example
1. Generates a default .env file with basic content, including a placeholder for your app name. Automatically checks if .env is listed in .gitignore and adds it if not already present.
dart run tarsier_env new
This will generate a .env file in the root directory with the following pre-defined content:
# AUTO-GENERATED FILE.
# YOU CAN EDIT/ADD MORE KEYS AND ITS VALUE.
# Generated by tarsier_env script.
APP_NAME="Tarsier"
APP_ENV=local
APP_KEY=null
APP_DEBUG=true
APP_URL=http://localhost
...
Above defined .ENV file is derived from Laravel's .env.example file.
The project directory structure will look like this.
your_project_name/
├── lib/
│ └── name.dart
├── test/
├── .env #This is the created file upon running the command
├── pubspec.yaml
├── ...
2. Generates a env.dart file containing static getters for environment variables from your .env file. Automatically imports env.dart. Inserts await Env.init(); in the main() function of main.dart.
dart run tarsier_env generate common/environment
- If no path is provided, the generated file will be placed in
lib/env.dart. - If a relative path under the
libdirectory is provided, the file will be placed in the corresponding subfolder. - Every time there are changes in
.envfile, it is required to run above command to re-generate theenv.dartfile.
This will create lib/common/environment/env.dart with the environment. After running above code, you can access the environment variables in your Flutter app.
The env.dart file generated by the package would look like this:
class Env {
static Map<String, String> _variables = {};
static init() async {
final content = await rootBundle.loadString('.env');
_variables = parseEnv(content);
}
static T get<T>(String key, [T? defaultValue]) {
final value = _variables[key];
if (value == null) return resolvedDefaultValue<T>(defaultValue);
return convertType<T>(value) ?? resolvedDefaultValue<T>(defaultValue);
}
static Map<String, String> get vars => _variables;
static String? get appName => _variables['APP_NAME'];
static String? get appKey => _variables['APP_KEY'];
}
In your main.dart, ensure the Env.init() method is called before using any environment variable.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'common/environment/env.dart'; // Automatically generated import
void main() async {
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
await Env.init(); // Initialize environment variables
String? appName = Env.appName; // You can directly access generated static variables
String? appKey = Env.vars['APP_KEY']; // Or you can use the key in the Map<String,String>
String appUrl = Env.get('APP_URL', 'http://localhost'); // Or you can use the get function with default fallback
// You can call also use "get" function with fallback value
int dbPort = Env.get<int>('DB_PORT', 3306);
bool appDebug = Env.get<bool>('APP_DEBUG', true);
double threshold = Env.get<double>('THRESHOLD', 3.1416);
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: Env.appName ?? 'Flutter App',
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(Env.vars['APP_NAME'] ?? 'Flutter App'),
),
),
);
}
}
🪪 Parsing output
- ✅ Keeps
#inside values if there’s no space before it - ✅ Removes inline comments only when a space exists before
# - ✅ Supports variable referencing (
${VAR_NAME}) - ✅ Handles concatenation (e.g.,
"${APP_URL}${APP_PATH}") - ✅ Ignores undefined variables, replacing with "" Instead
- ✅ Removes quotes & skips comments Properly
| Env Entry | Parse Output |
|---|---|
APP_NAME="Flutter System" |
Flutter System |
APP_ENV=local |
local |
APP_KEY="qwbNB#OzGbS95Q=" |
qwbNB#OzGbS95Q= |
APP_SCHEME=http |
http |
APP_DOMAIN=localhost #This is domain name |
localhost |
APP_URL="${APP_SCHEME}://${APP_DOMAIN}" |
http://localhost |
APP_PATH=/api/v1 |
/api/v1 |
APP_ENDPOINT="${APP_URL}${APP_PATH}" |
http://localhost/api/v1 |
📸 Example Screenshots
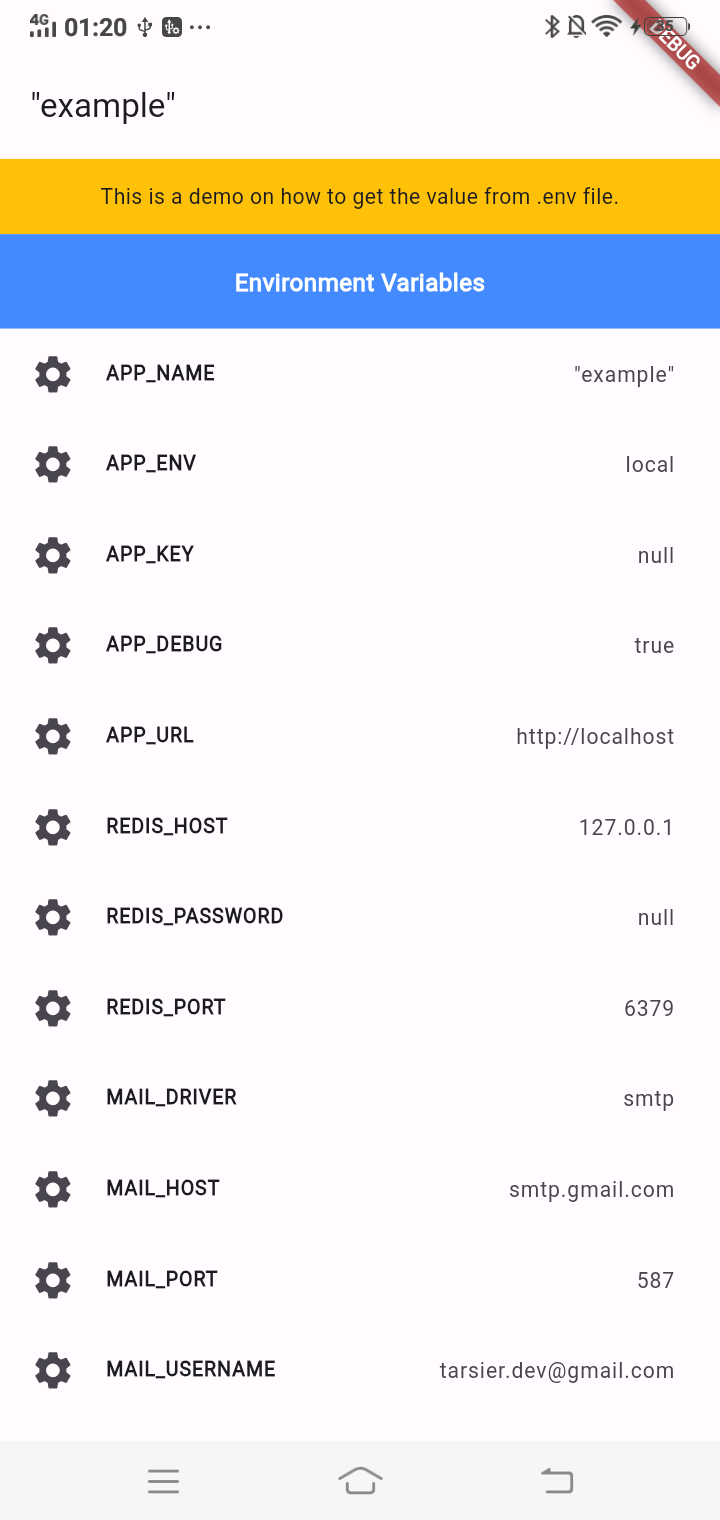
🎖️ License
This package is licensed under the MIT License.
🐞Suggestions for Improvement?
Feel free to open an issue or submit a pull request on GitHub.
Why "Tarsier ENV"?
The tarsier, one of the smallest primates, symbolizes simplicity and adaptability—just like this package! 🐒
Libraries
- tarsier_env
- This library provides tools for loading and managing environment variables
from
.envfiles in Dart and Flutter applications. It helps developers store configuration settings, such as API keys or database credentials, outside the source code.




