utopia_localization_generator
Utopia USS libs - Localization - Google Sheet-based localization code generator.
Based on flutter_sheet_localization_generator
Install
Run the following command in your project directory:
$ flutter pub add utopia_localization_annotation utopia_localization_utils dev:utopia_localization_generator dev:build_runner
Usage
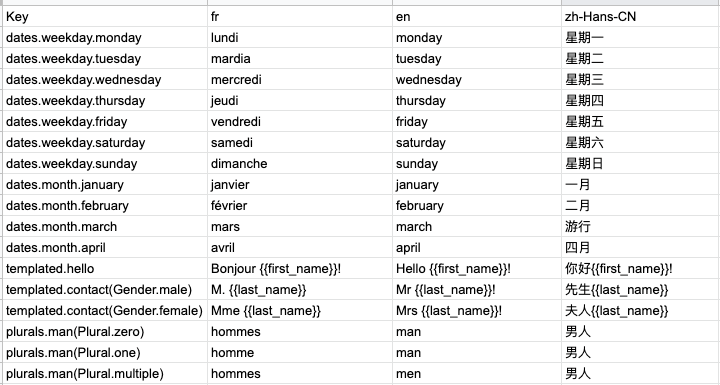
1. Create a Google Sheet
Create a sheet with your translations (using the format below, an example sheet is available here) :
Make sure your sheet is shared:
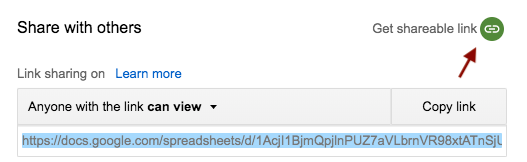
Extract from the link the DOCID and SHEETID
values: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/<DOCID>/edit#gid=<SHEETID>):
2. Create a localization file
Create a localization.dart file that will contain the generated models and data:
// See 1. to get DOCID and SHEETID
// The last parameter is the generated version. You must increment it each time you want to regenerate
// a new version of the labels.
@UtopiaLocalization("DOCID", "SHEETID", 1)
library;
import 'package:utopia_localization_annotation/utopia_localization_annotation.dart';
part 'localization.g.dart';
By default, the following will be generated:
- An
AppLocalizationsDatamodel class with fields/sub-models for all keys from the sheet. - An
appLocalizationsDataglobal constant with an instance ofAppLocalizationsDatafor every supported locale. - fromJson
/toJson` methods for all model classes.
3. Configure your app
Configure your app to use the generated localizations by making the modifications to your root App file:
import 'package:utopia_localization_utils/utopia_localization_utils.dart';
import 'localization.dart'; // Your localization file
extension BuildContextAppLocalizationsExtension on BuildContext {
AppLocalizationsData get strings => localizations();
}
class App extends StatelessWidget {
//...
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
supportedLocales: appLocalizationsData.supportedLocales,
localizationsDelegates: [
const UtopiaLocalizationsDelegate(appLocalizationsData),
// ... other delegates, like the default Flutter ones:
GlobalMaterialLocalizations.delegate,
GlobalWidgetsLocalizations.delegate,
],
// ...
);
}
}
4. Generate & use your localizations
Trigger code generation using: dart run build_runner build or dart run build_runner watch.
Now you can access your localizations from anywhere in your app using context.strings.<key>.
Re-generation
Because of the caching system of build_runner, it can't detect if there's a change on the distant sheet, and it can't
know if a new generation is needed.
The third version parameter of the @UtopiaLocalization annotation solves this issue.
Each time you want to trigger a new generation, simply increment that version number and call the build runner again.
Google Sheet format
You can see an example sheet here.
Global format
The file should have :
- A first header row
- Column 0 : "Key"
- then each supported language code ("en", "fr", ...)
- Following rows for labels
- Column 0 : the label key (can be a hierarchy, separated by dots)
- then each translation based on language code of the column
Ignoring a column
Sometimes you may need to add comments for translators. For this, simply add a column with a name between parenthesis, and the column will be completely ignored by the generator.
Example :
| Key | (Comments) | fr | en |
|---|---|---|---|
| example.man(Gender.male) | This is a man title on home page | homme | man |
| example.man(Gender.female) | This is a woman title on home page | femme | woman |
Conditionals
It is pretty common to have variants of a label based on a parameter (like a user's gender, or a given month number).
Simply duplicate your entries and end them with (value), where value can be any valid Dart constant value (including
enum values, strings, integers and even records). If a duplicated entry without a condition is present, it will be used
as a default value.
| Key | fr | en |
|---|---|---|
| example.man(Gender.male) | homme | man |
| example.man(Gender.female) | femme | woman |
| example.man | personne | person |
| example.month(0) | janivier | january |
| example.month(1) | février | february |
Then, in Dart a function accepting the condition as a parameter will be generated:
context.strings.example.man(user.hasGender ? user.gender : null);
context.strings.example.month(DateTime.now().month);
If passed value doesn't match any present condition, the default value will be used; if default value is not present, an exception will be thrown.
See example for more details.
Parameters
You can insert a {{KEY}} template into a translation value to have dynamic labels.
A Dart function will be generated to be used from your code.
/// Sheet
values.hello | "Hello {{firstName}}!"
/// Code
print(labels.values.hello(firstName: "World"));
Typed parameters
You can also add one of the compatible types (int, double, num, DateTime) to the parameter by suffixing its key
with :<type>.
/// Sheet
values.price, "The price is {{price:double}}\$"
/// Code
print(labels.values.price(price: 10.5));
Formatted parameters
You can indicate how the templated value must be formatted by ending the value with a formatting rule in
brackets [<rule-key>]. This can be particularly useful for typed parameters.
The available formatting rules depend on the type and generally rely on the intl package.
| Type | rule-key | Generated code |
|---|---|---|
double, int, num |
decimalPercentPattern, currency, simpleCurrency, compact, compactLong, compactSimpleCurrency, compactCurrency, decimalPattern, percentPattern, scientificPattern |
NumberFormat.<rule-key>(...) |
DateTime |
Any date format valid pattern | DateFormat('<rule-key>', ...).format(...) |
Examples:
/// Sheet
values.price | "Price : {{price:double[compactCurrency]}}"
/// Code
print(labels.values.price(price: 2.00));
/// Sheet
values.today | "Today : {{date:DateTime[EEE, M/d/y]}}"
/// Code
print(labels.values.today(date: DateTime.now()));
Changing labels at runtime
By default, fromJson/toJson methods are generated for all localization classes. This allows them to be serialized
and de-serialized at runtime, which makes it possible to change the labels without having to recompile the app.
See example for a basic implementation that exports/imports from a JSON file.