connectivity_plus 0.8.0  connectivity_plus: ^0.8.0 copied to clipboard
connectivity_plus: ^0.8.0 copied to clipboard
Flutter plugin for discovering the state of the network (WiFi & mobile/cellular) connectivity on Android and iOS.
connectivity_plus #
This plugin allows Flutter apps to discover network connectivity and configure themselves accordingly. It can distinguish between cellular vs WiFi connection. This plugin works for iOS and Android.
Note that on Android, this does not guarantee connection to Internet. For instance, the app might have wifi access but it might be a VPN or a hotel WiFi with no access.
Usage #
Sample usage to check current status:
import 'package:connectivity_plus/connectivity.dart';
var connectivityResult = await (Connectivity().checkConnectivity());
if (connectivityResult == ConnectivityResult.mobile) {
// I am connected to a mobile network.
} else if (connectivityResult == ConnectivityResult.wifi) {
// I am connected to a wifi network.
}
Note that you should not be using the current network status for deciding whether you can reliably make a network connection. Always guard your app code against timeouts and errors that might come from the network layer.
You can also listen for network state changes by subscribing to the stream exposed by connectivity plugin:
import 'package:connectivity_plus/connectivity.dart';
@override
initState() {
super.initState();
subscription = Connectivity().onConnectivityChanged.listen((ConnectivityResult result) {
// Got a new connectivity status!
})
}
// Be sure to cancel subscription after you are done
@override
dispose() {
super.dispose();
subscription.cancel();
}
Note that connectivity changes are no longer communicated to Android apps in the background starting with Android O. You should always check for connectivity status when your app is resumed. The broadcast is only useful when your application is in the foreground.
You can get wi-fi related information using:
import 'package:connectivity_plus/connectivity.dart';
var wifiBSSID = await (Connectivity().getWifiBSSID());
var wifiIP = await (Connectivity().getWifiIP());network
var wifiName = await (Connectivity().getWifiName());wifi network
iOS 12 #
To use .getWifiBSSID() and .getWifiName() on iOS >= 12, the Access WiFi information capability in XCode must be enabled. Otherwise, both methods will return null.
iOS 13 #
The methods .getWifiBSSID() and .getWifiName() utilize the CNCopyCurrentNetworkInfo function on iOS.
As of iOS 13, Apple announced that these APIs will no longer return valid information. An app linked against iOS 12 or earlier receives pseudo-values such as:
-
SSID: "Wi-Fi" or "WLAN" ("WLAN" will be returned for the China SKU).
-
BSSID: "00:00:00:00:00:00"
An app linked against iOS 13 or later receives null.
The CNCopyCurrentNetworkInfo will work for Apps that:
-
The app uses Core Location, and has the user’s authorization to use location information.
-
The app uses the NEHotspotConfiguration API to configure the current Wi-Fi network.
-
The app has active VPN configurations installed.
If your app falls into the last two categories, it will work as it is. If your app doesn't fall into the last two categories, and you still need to access the wifi information, you should request user's authorization to use location information.
There is a helper method provided in this plugin to request the location authorization: requestLocationServiceAuthorization.
To request location authorization, make sure to add the following keys to your Info.plist file, located in <project root>/ios/Runner/Info.plist:
NSLocationAlwaysAndWhenInUseUsageDescription- describe why the app needs access to the user’s location information all the time (foreground and background). This is called Privacy - Location Always and When In Use Usage Description in the visual editor.NSLocationWhenInUseUsageDescription- describe why the app needs access to the user’s location information when the app is running in the foreground. This is called Privacy - Location When In Use Usage Description in the visual editor.
Limitations on the web platform #
In order to retrieve information about the quality/speed of a browser's connection, the web implementation of the connectivity plugin uses the browser's NetworkInformation Web API, which as of this writing (June 2020) is still "experimental", and not available in all browsers:
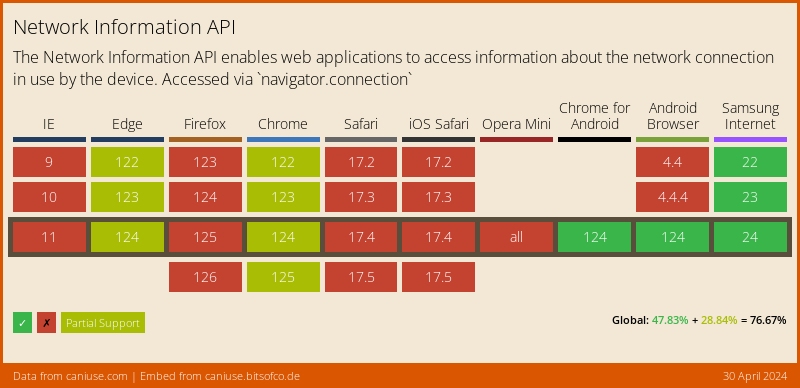
On desktop browsers, this API only returns a very broad set of connectivity statuses (One of 'slow-2g', '2g', '3g', or '4g'), and may not provide a Stream of changes. Firefox still hasn't enabled this feature by default.
Fallback to navigator.onLine
For those browsers where the NetworkInformation Web API is not available, the plugin falls back to the NavigatorOnLine Web API, which is more broadly supported:
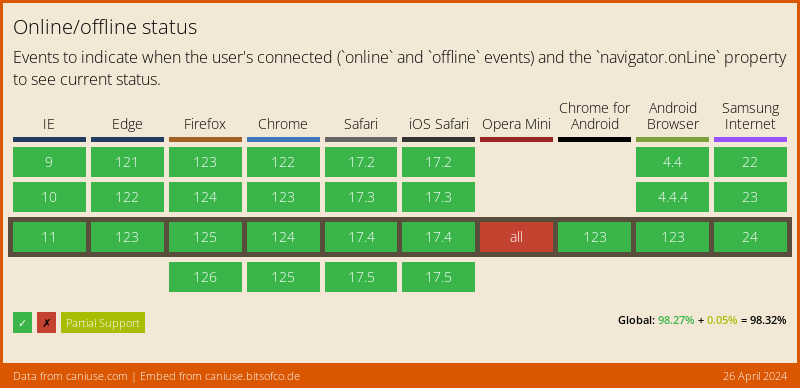
The NavigatorOnLine API is provided by dart:html, and only supports a boolean connectivity status (either online or offline), with no network speed information. In those cases the plugin will return either wifi (when the browser is online) or none (when it's not).
Other than the approximate "downlink" speed, where available, and due to security and privacy concerns, no Web browser will provide any specific information about the actual network your users' device is connected to, like the SSID on a Wi-Fi, or the MAC address of their device.
Getting Started #
For help getting started with Flutter, view our online documentation.
For help on editing plugin code, view the documentation.