contained_tab_bar_view 0.4.0  contained_tab_bar_view: ^0.4.0 copied to clipboard
contained_tab_bar_view: ^0.4.0 copied to clipboard
ContainedTabBarView encapsulates TabController, TabBar and TabBarView into a single, easy to use Widget.
ContainedTabBarView #
ContainedTabBarView encapsulates TabController, TabBar and TabBarView into a single, easy to use, constrainable Widget.
Usage #
To use this package, add contained_tab_bar_view as a dependency in your pubspec.yaml file.
Examples #
All of the below examples can be found under "Examples", each written as a simple StatelessWidget.
Basic #
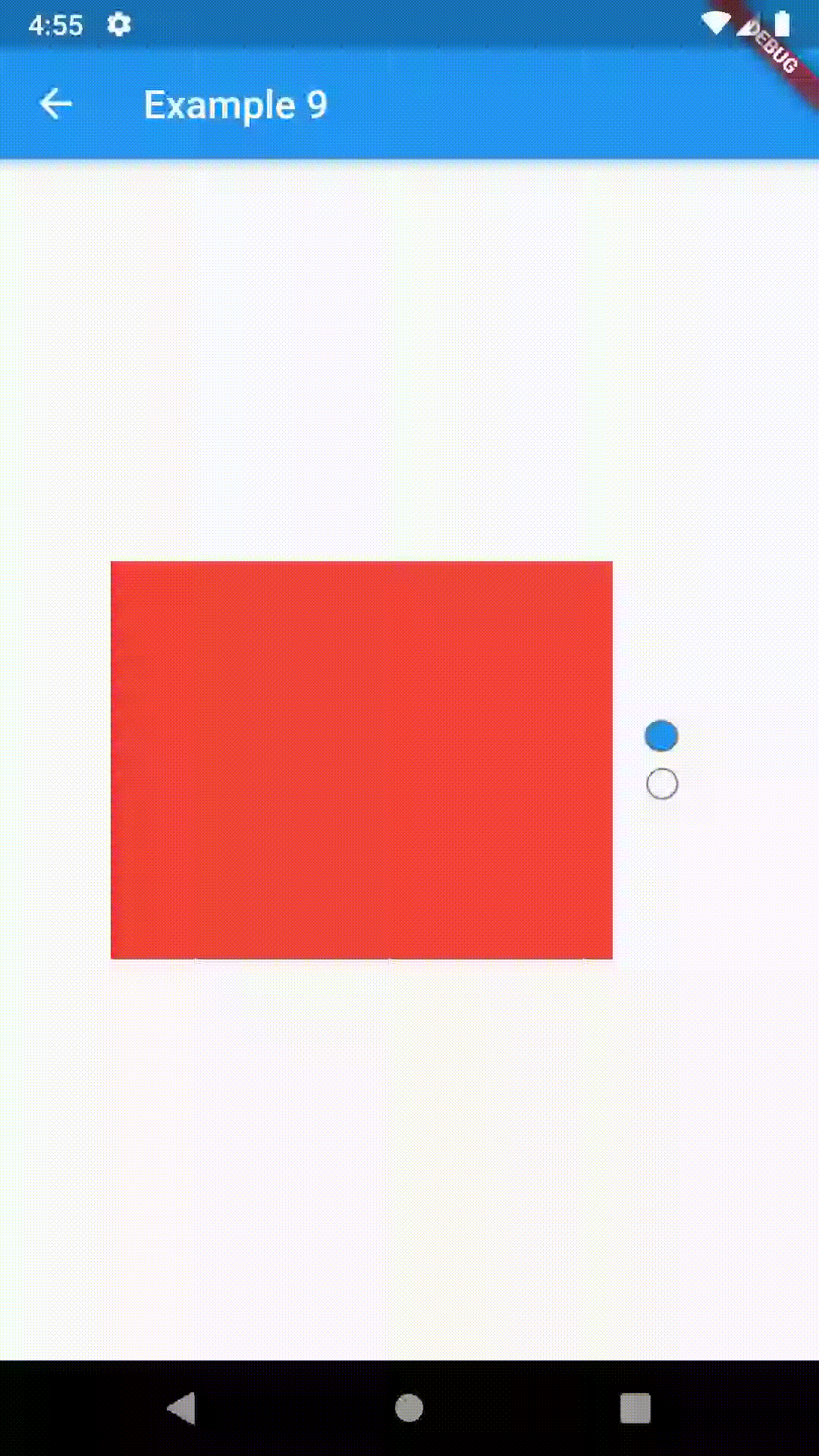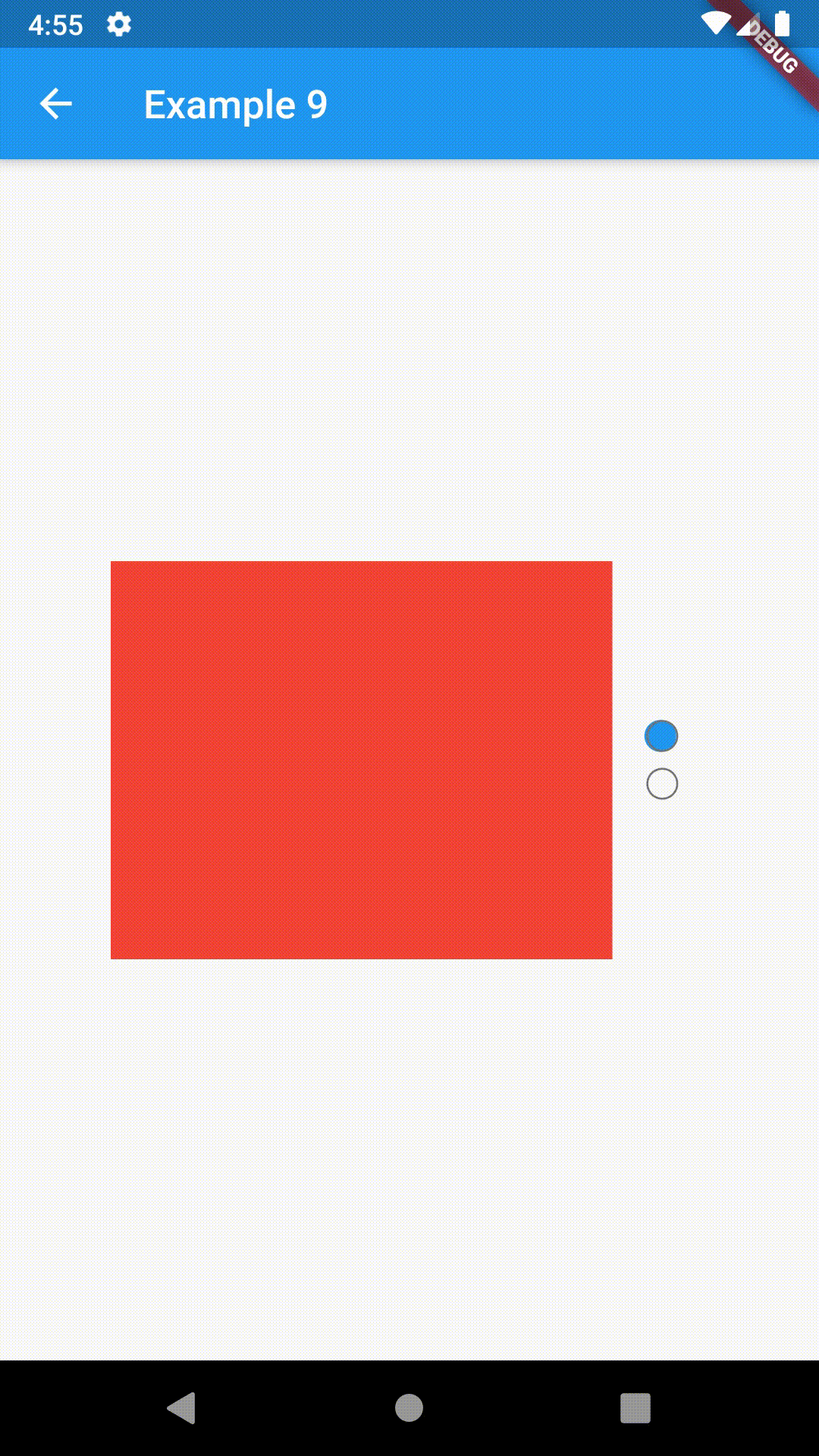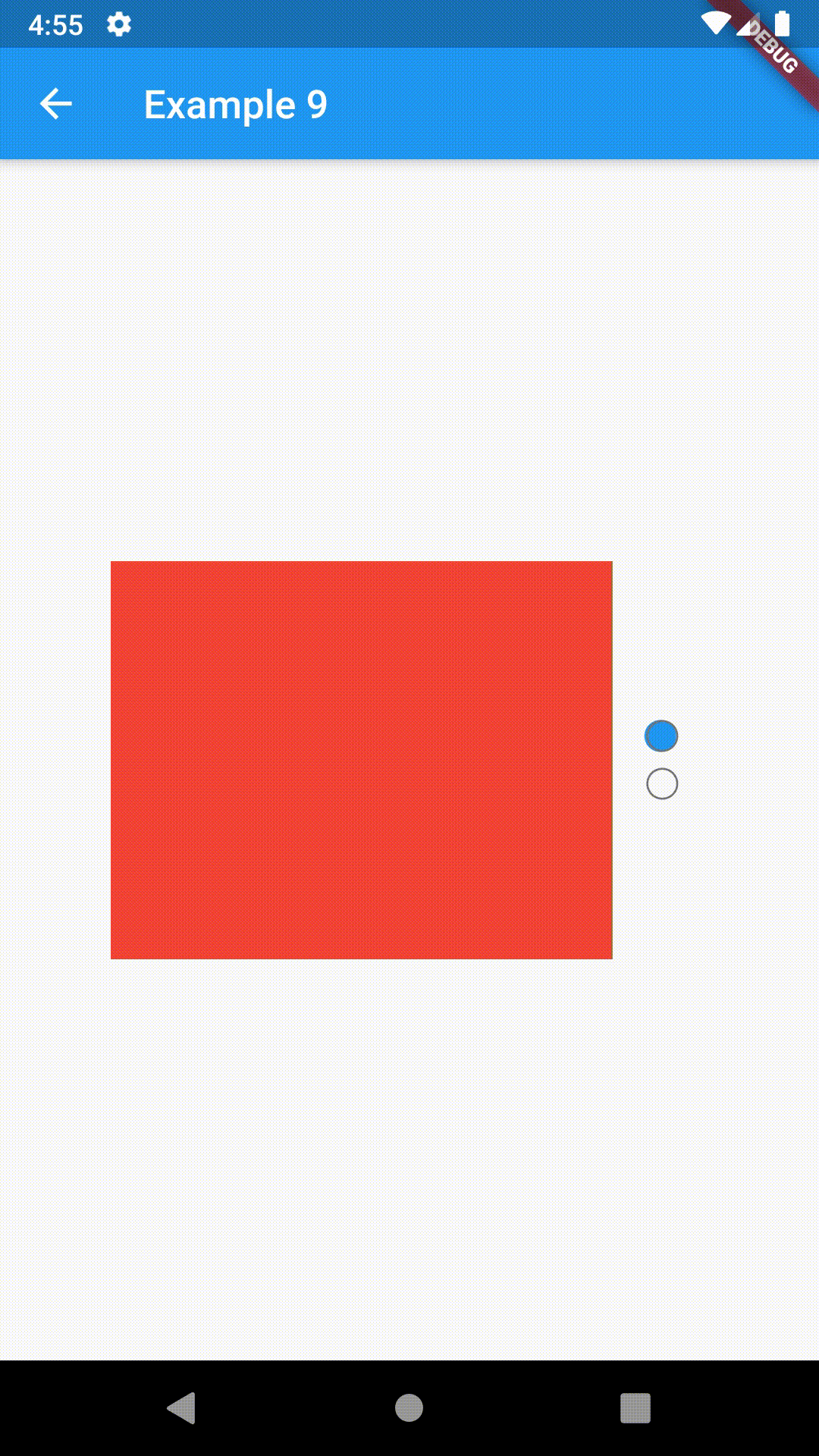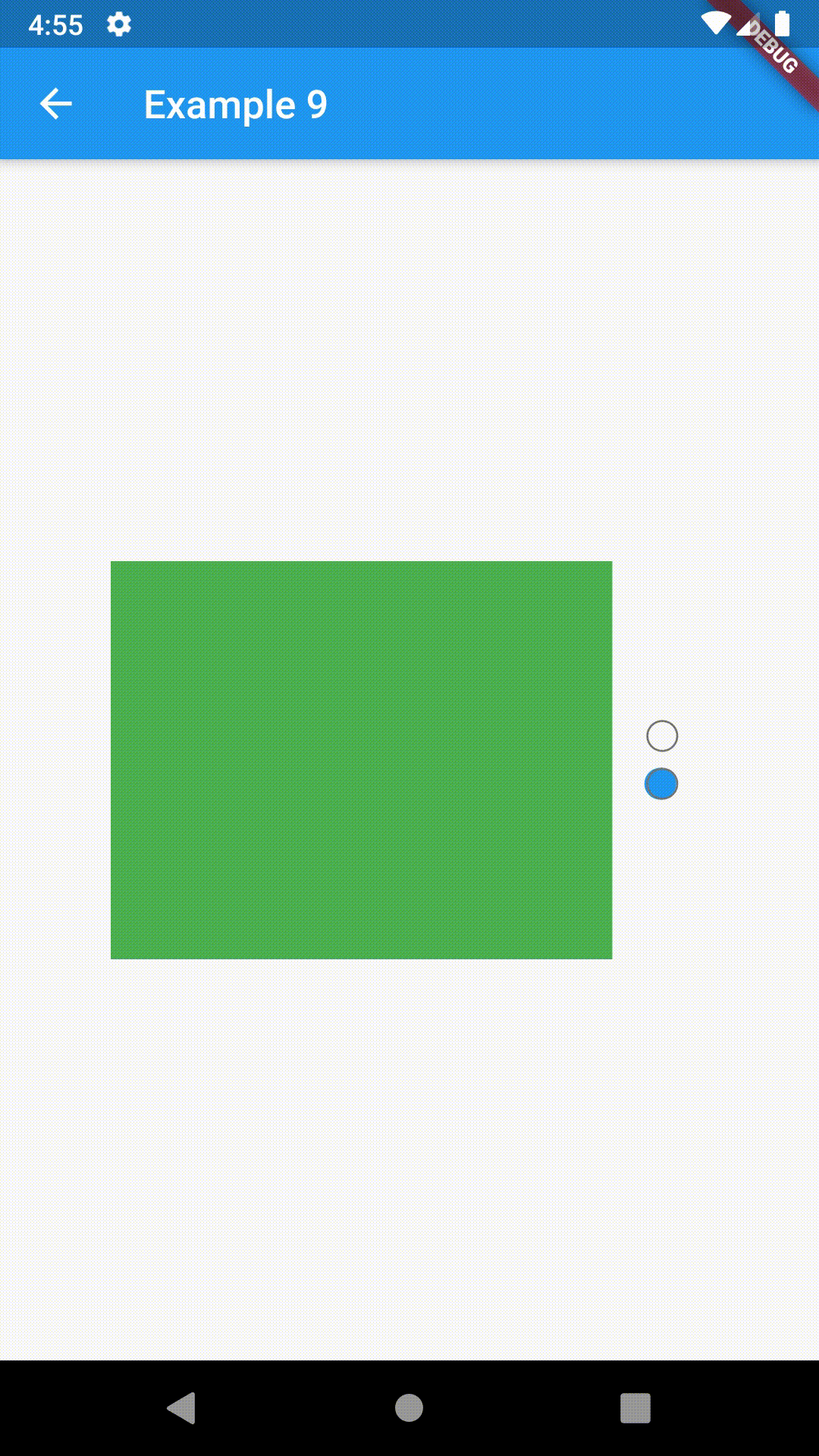
Basic examples include putting a ContainedTabBarView into a Container whose constraints will it obey. Putting a ContainedTabBarView directly into a body of a Scaffold will, expectedly, draw it full-screen.
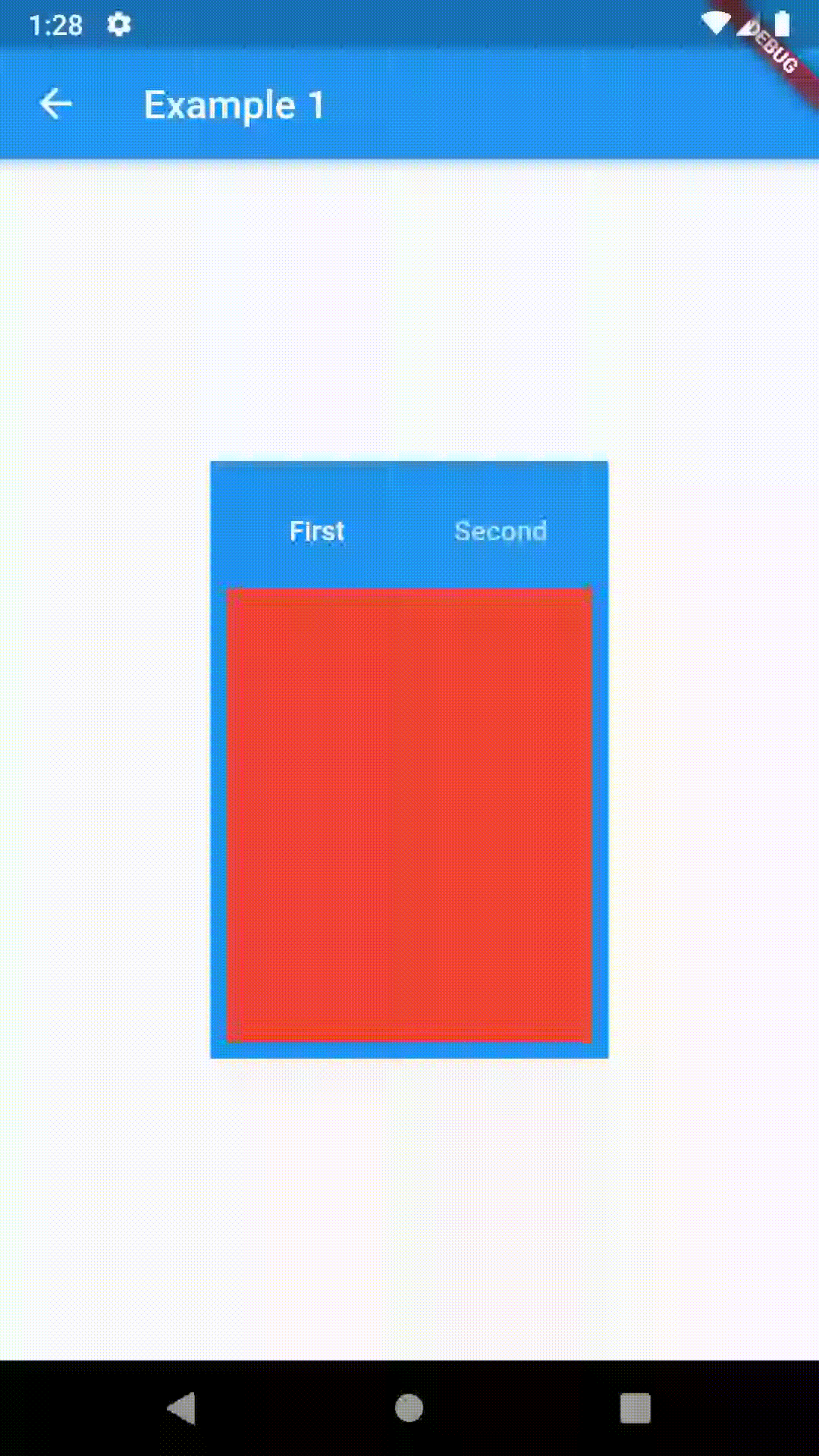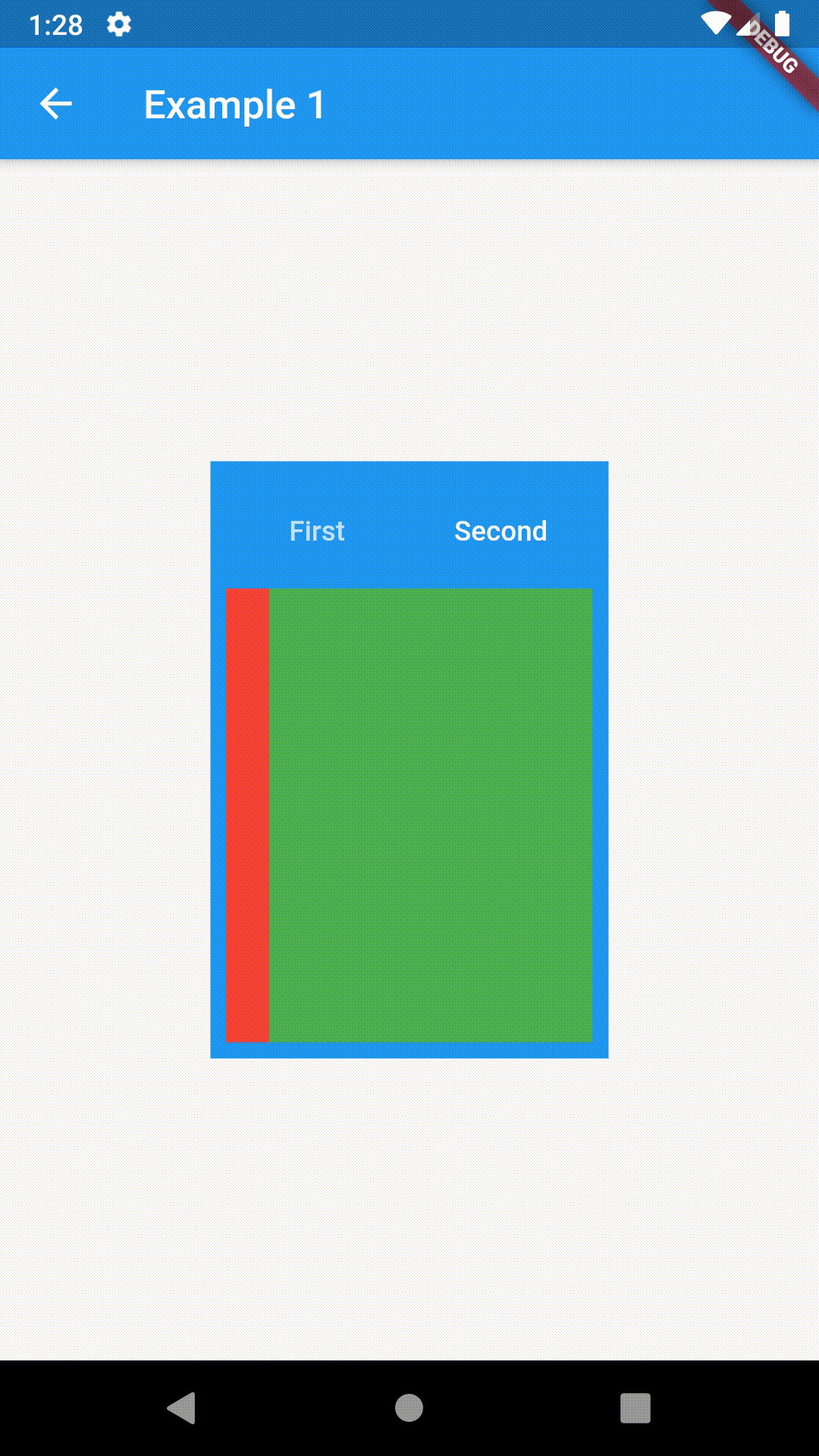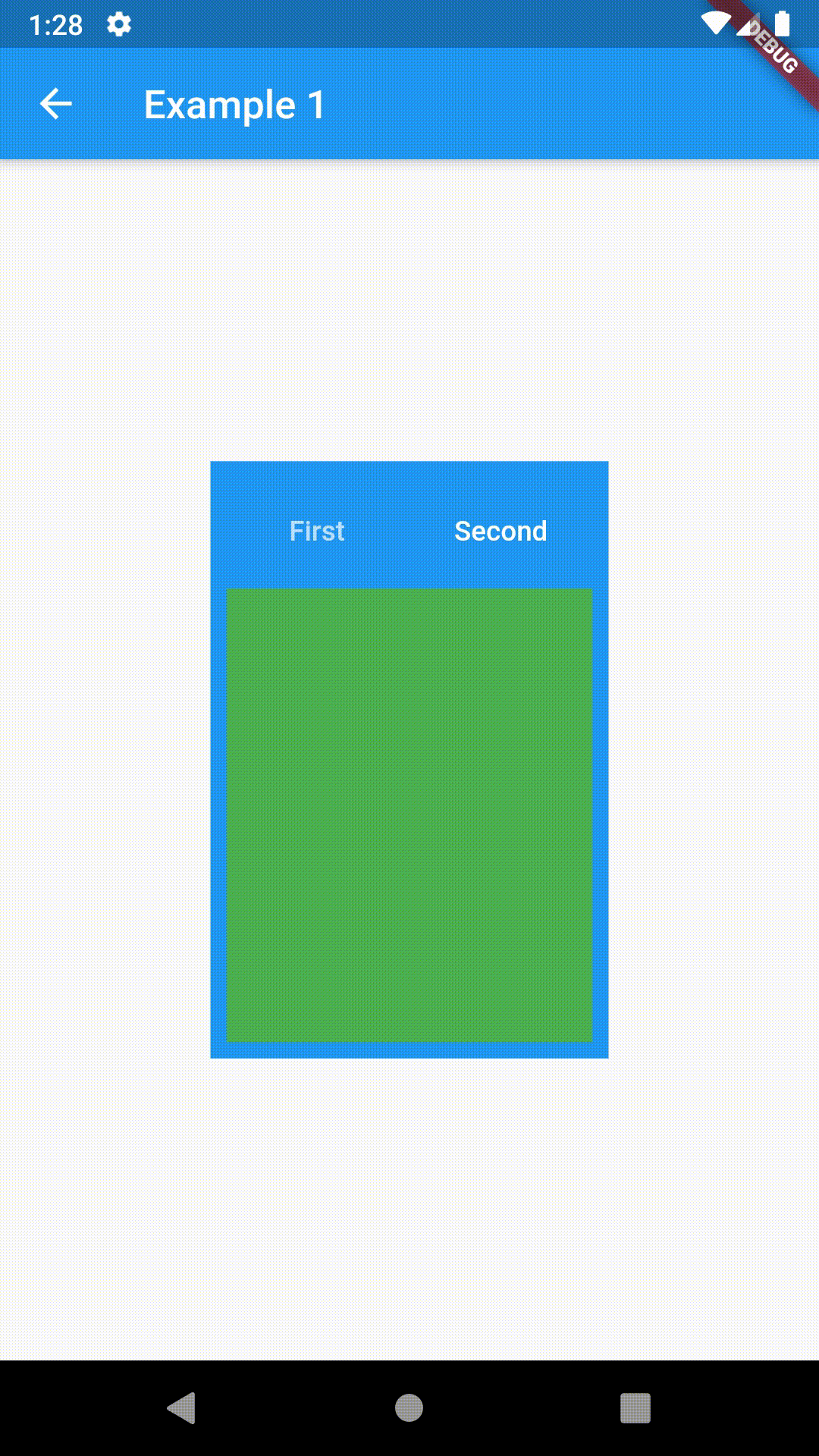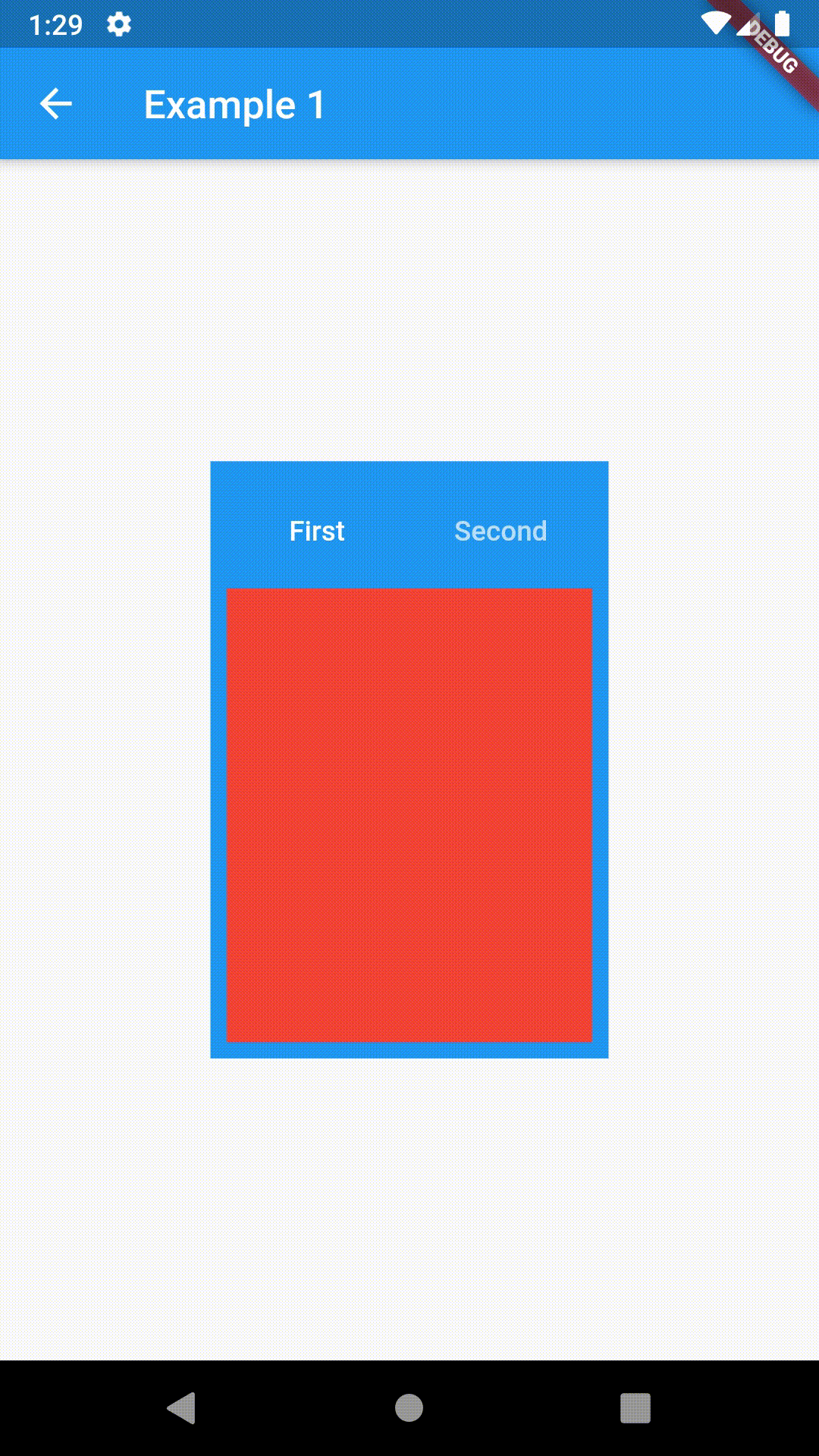
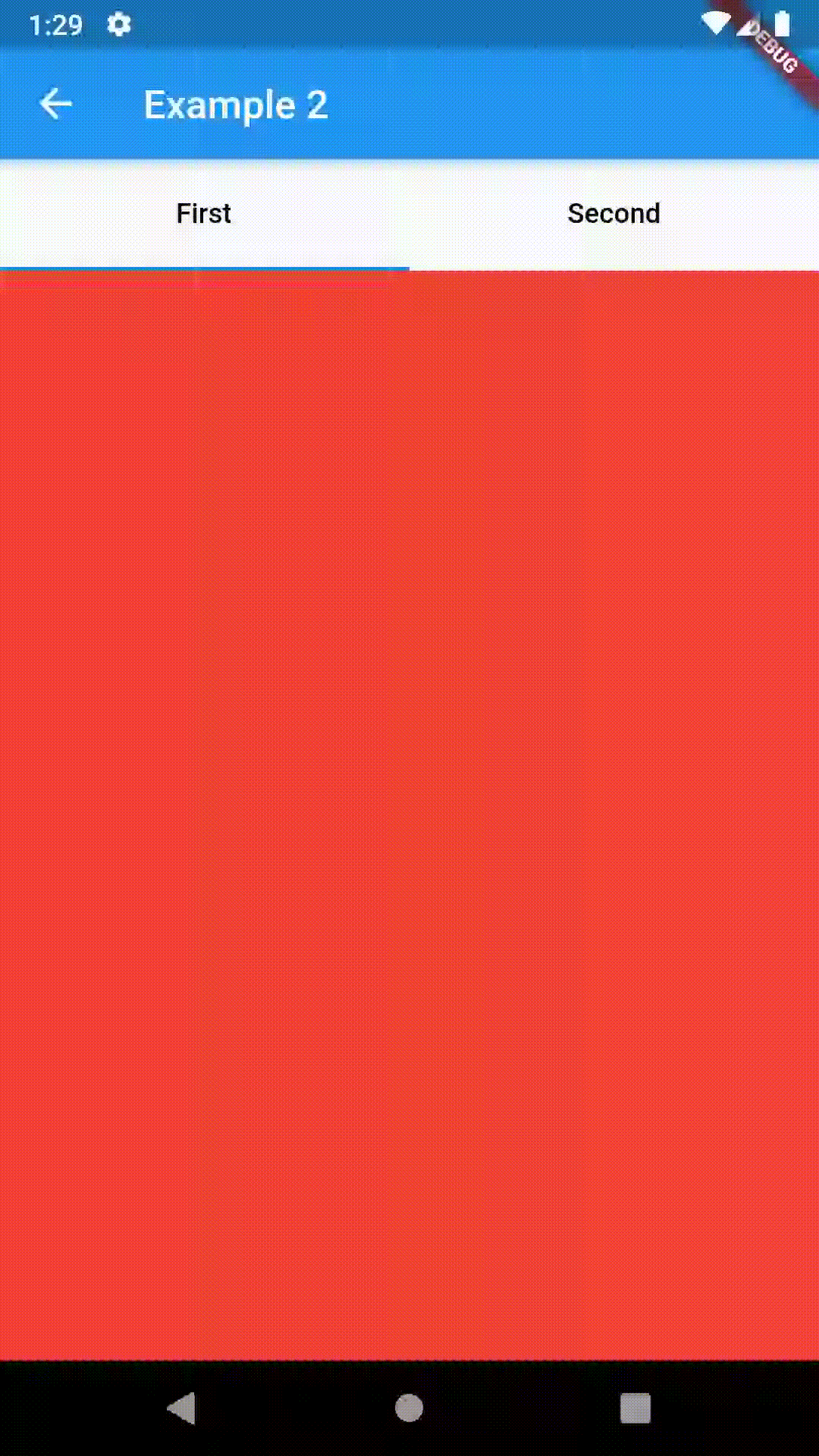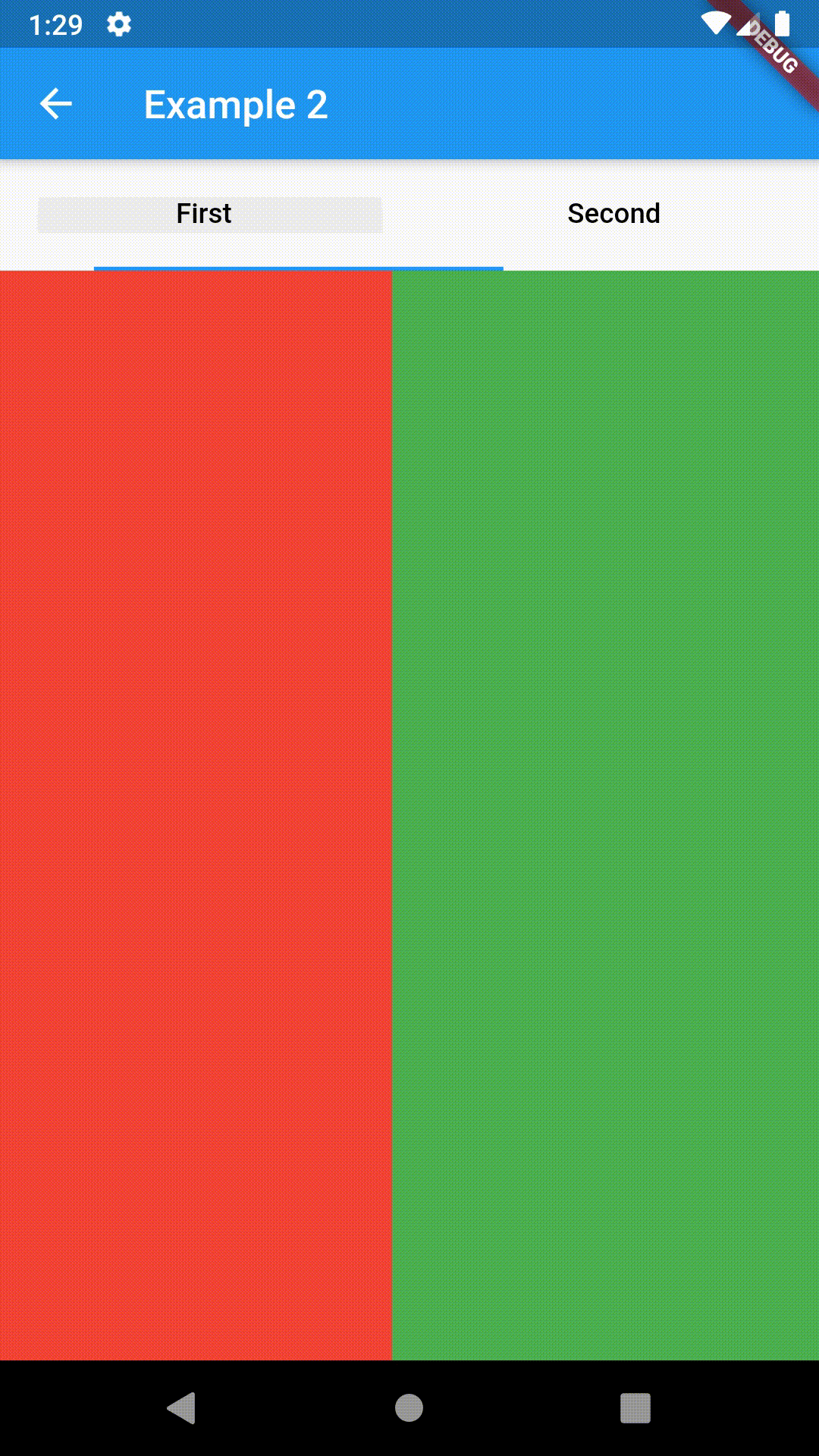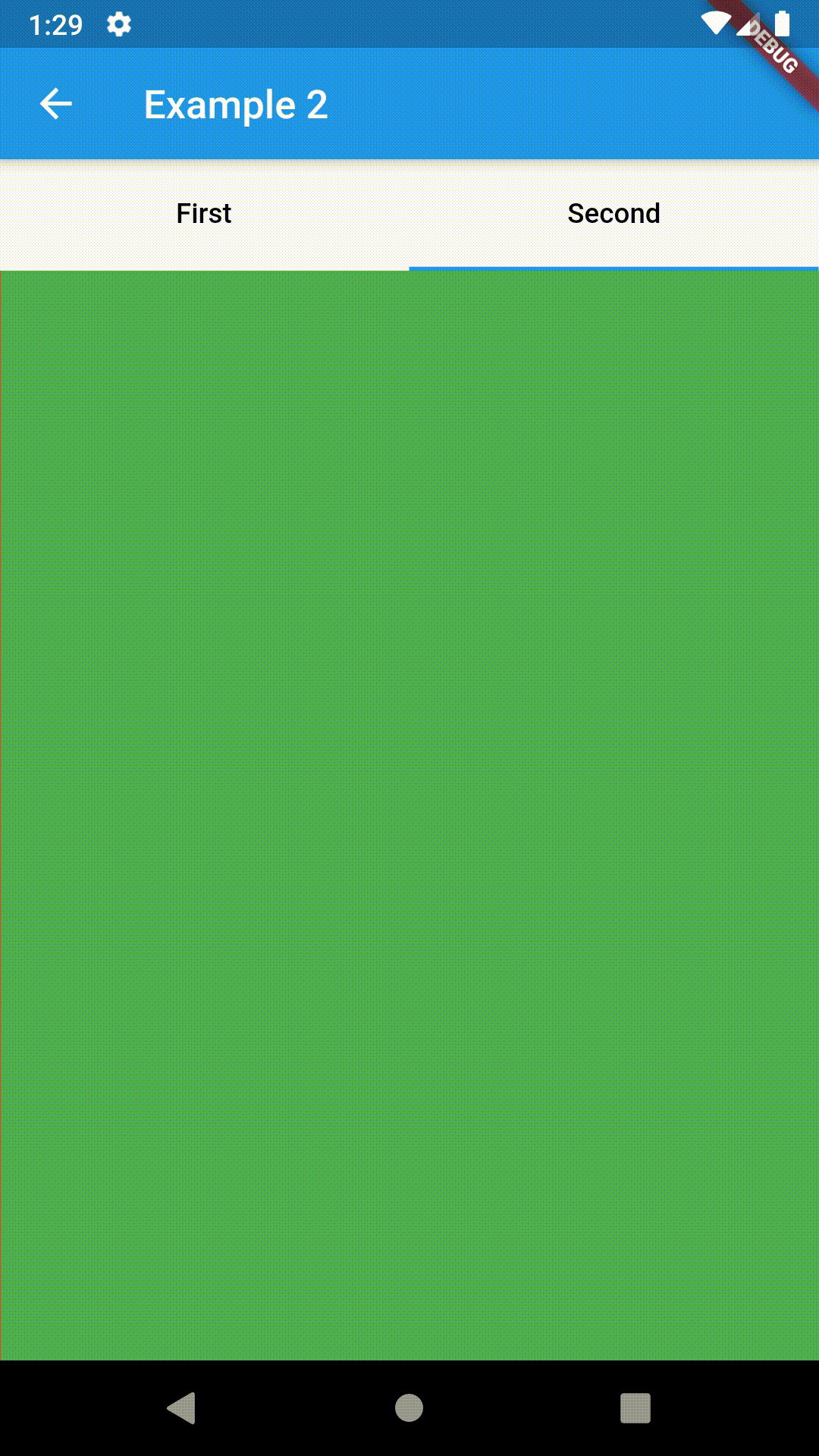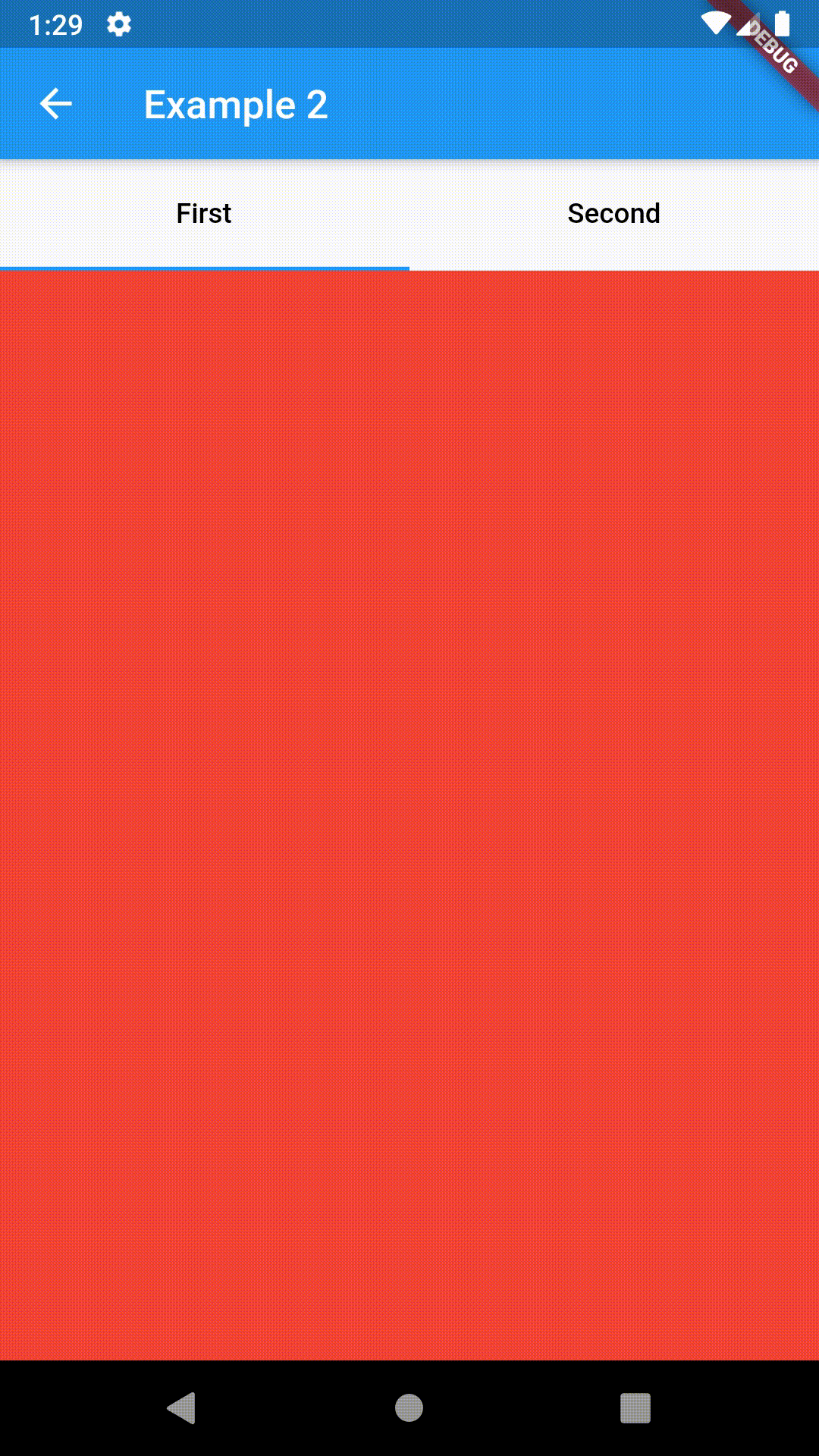
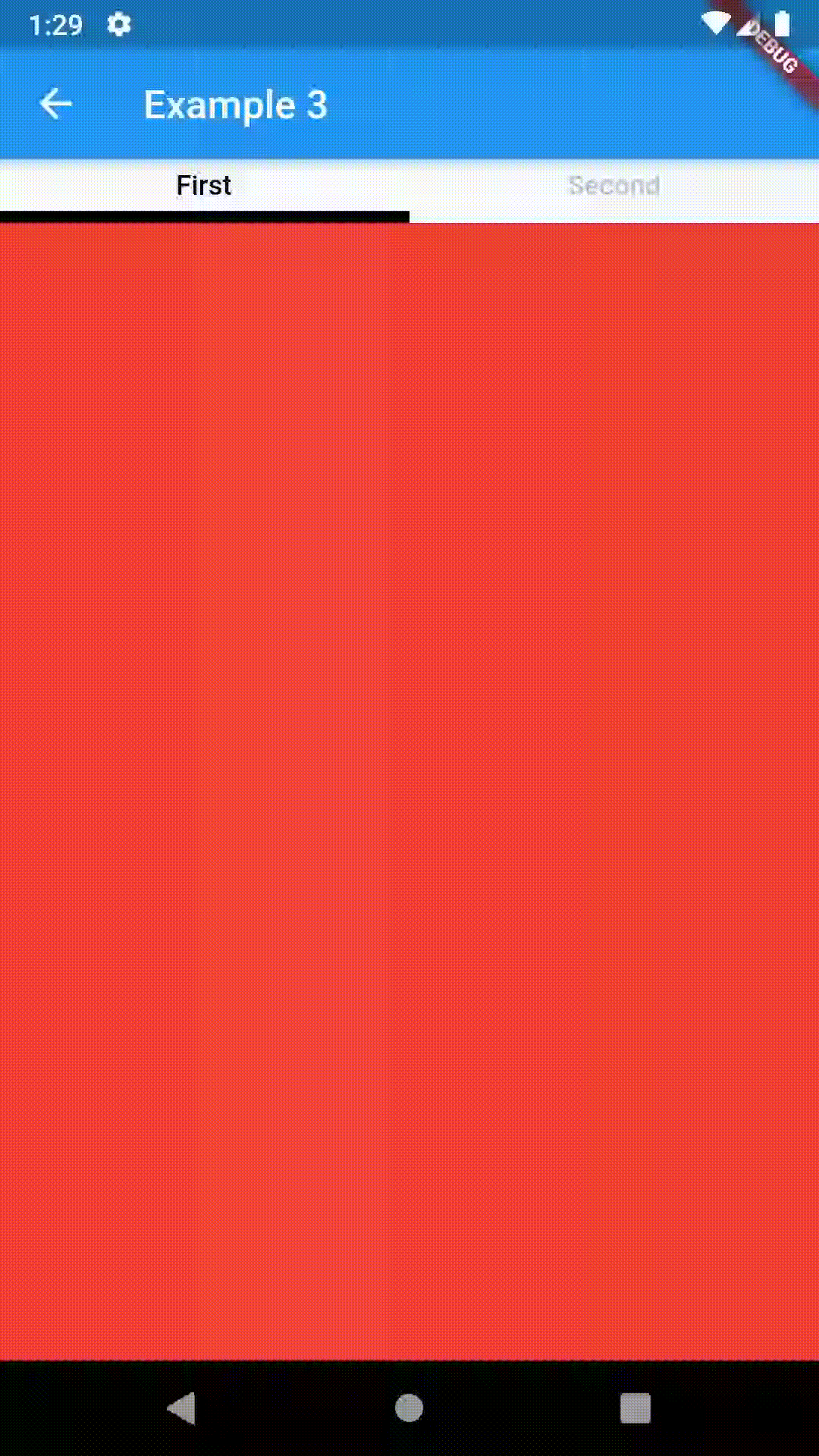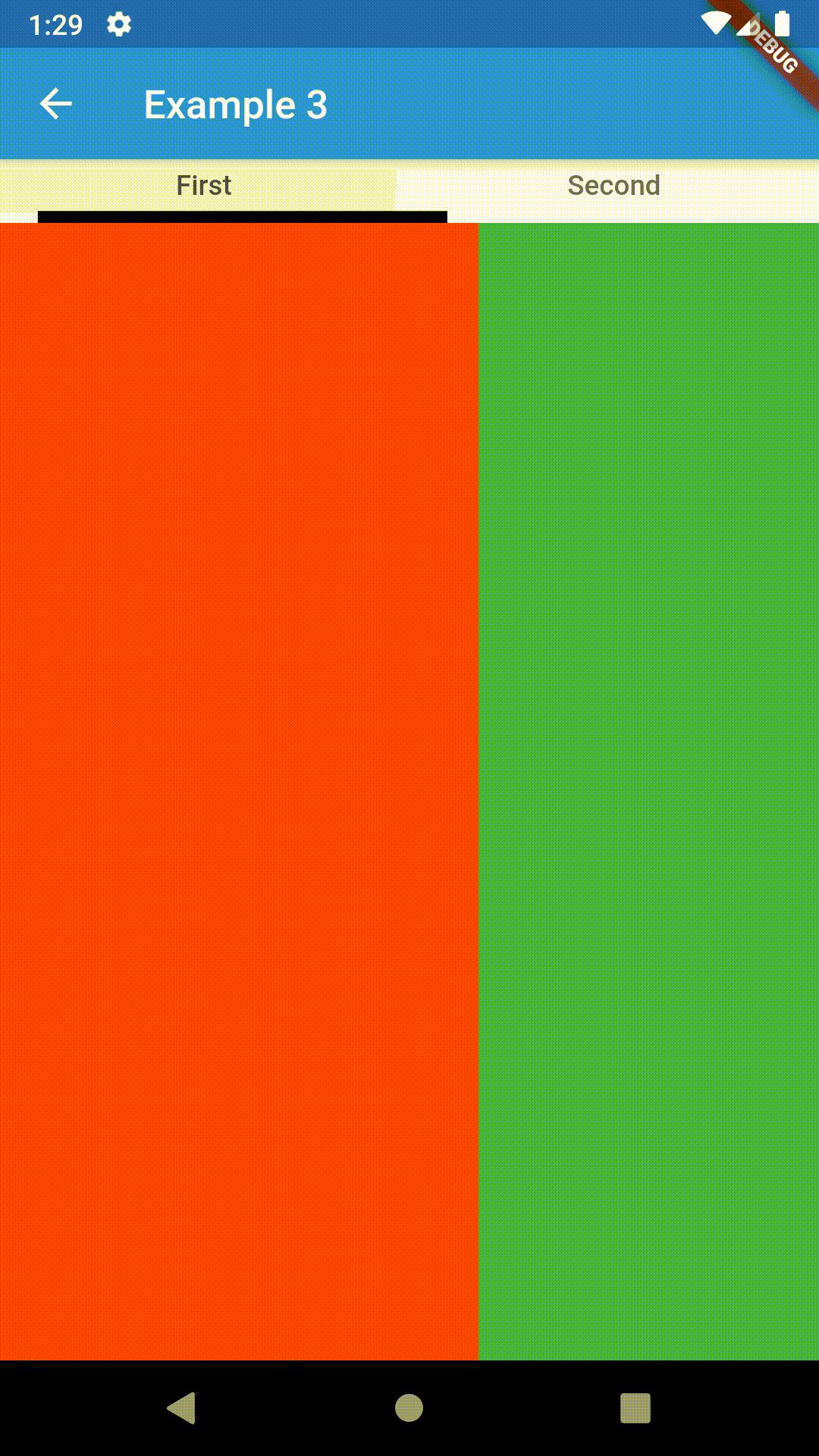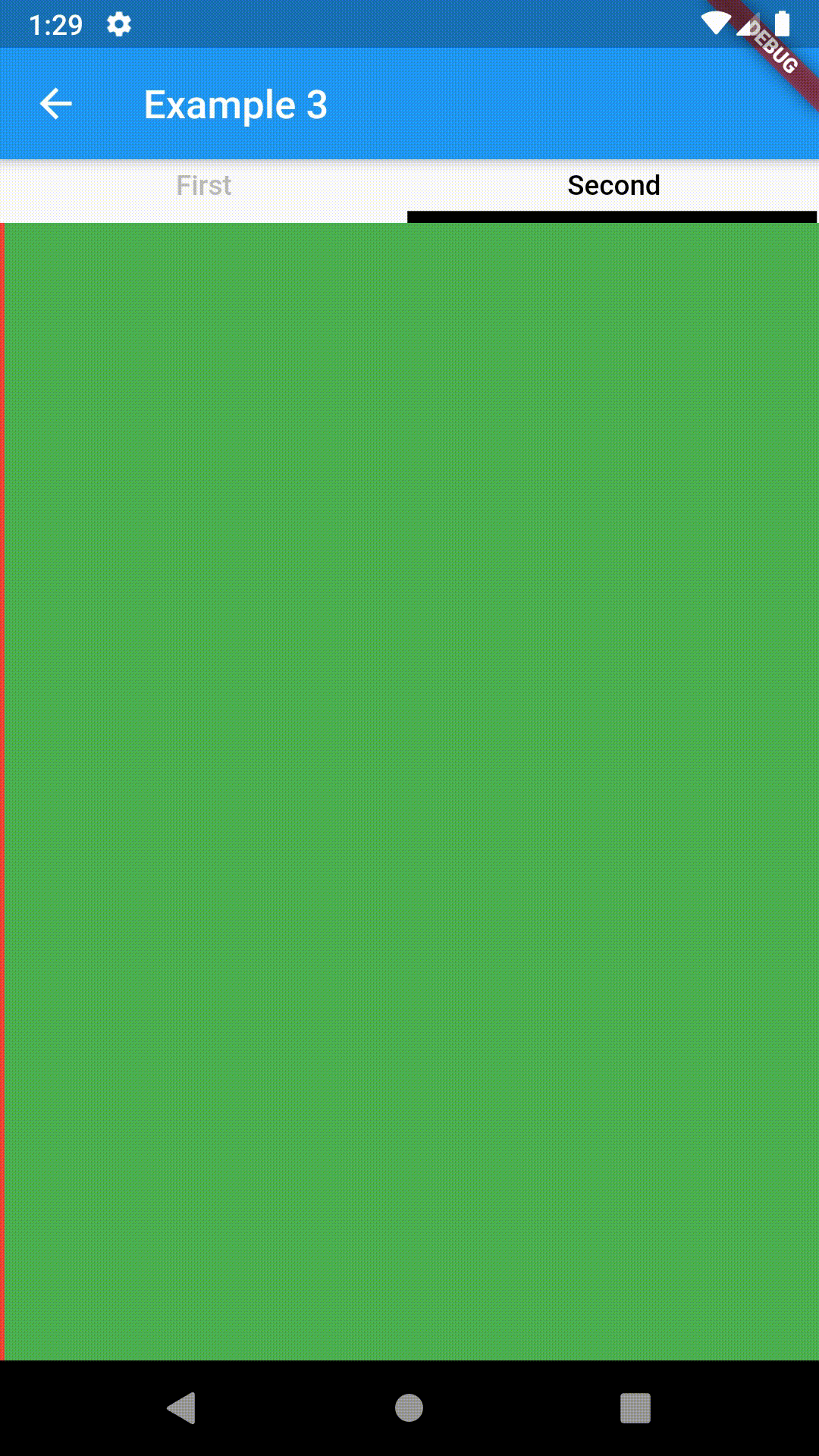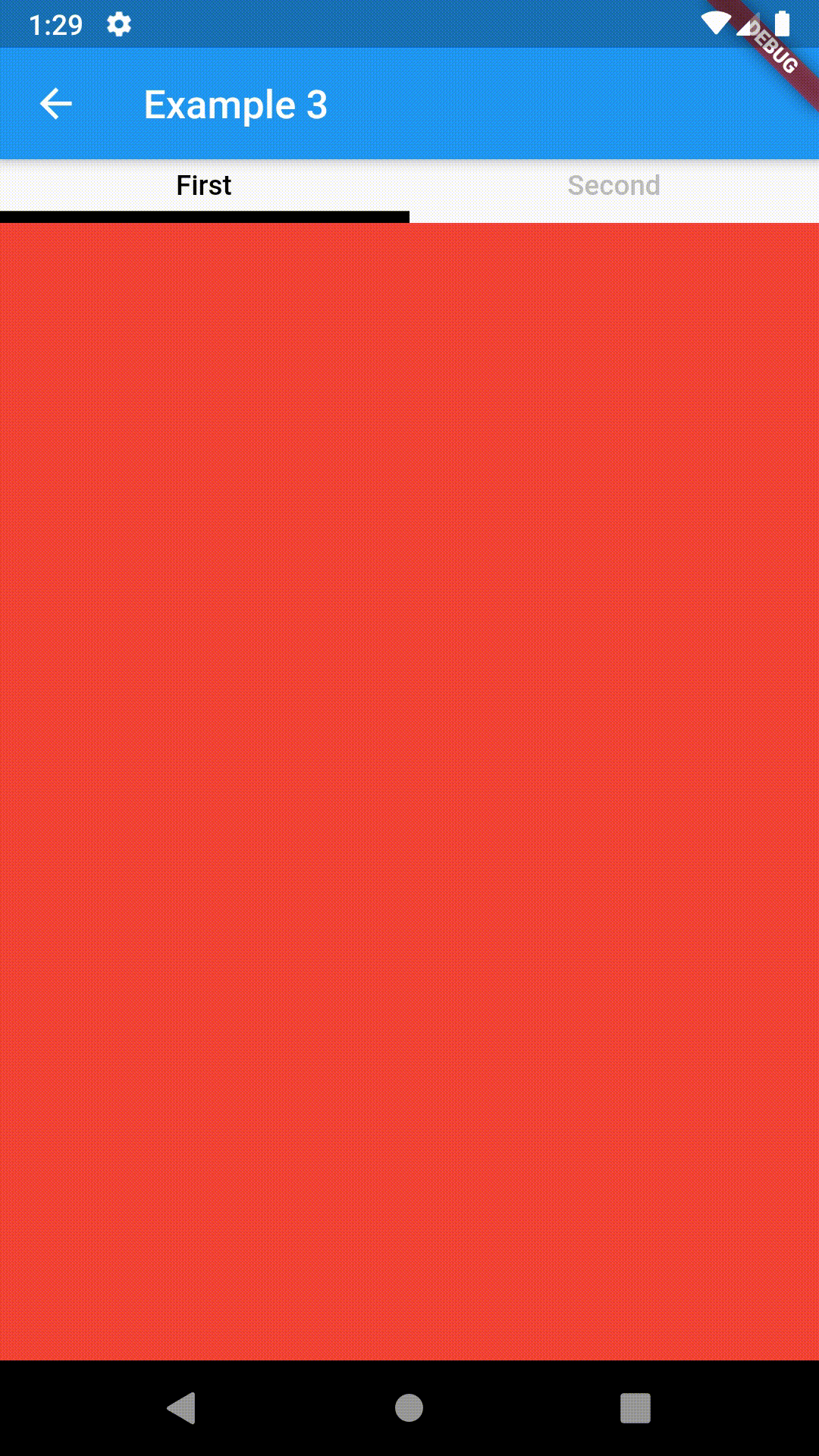
// Example 1
import 'package:contained_tab_bar_view/contained_tab_bar_view.dart';
...
Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
color: Colors.blue,
width: 200,
height: 300,
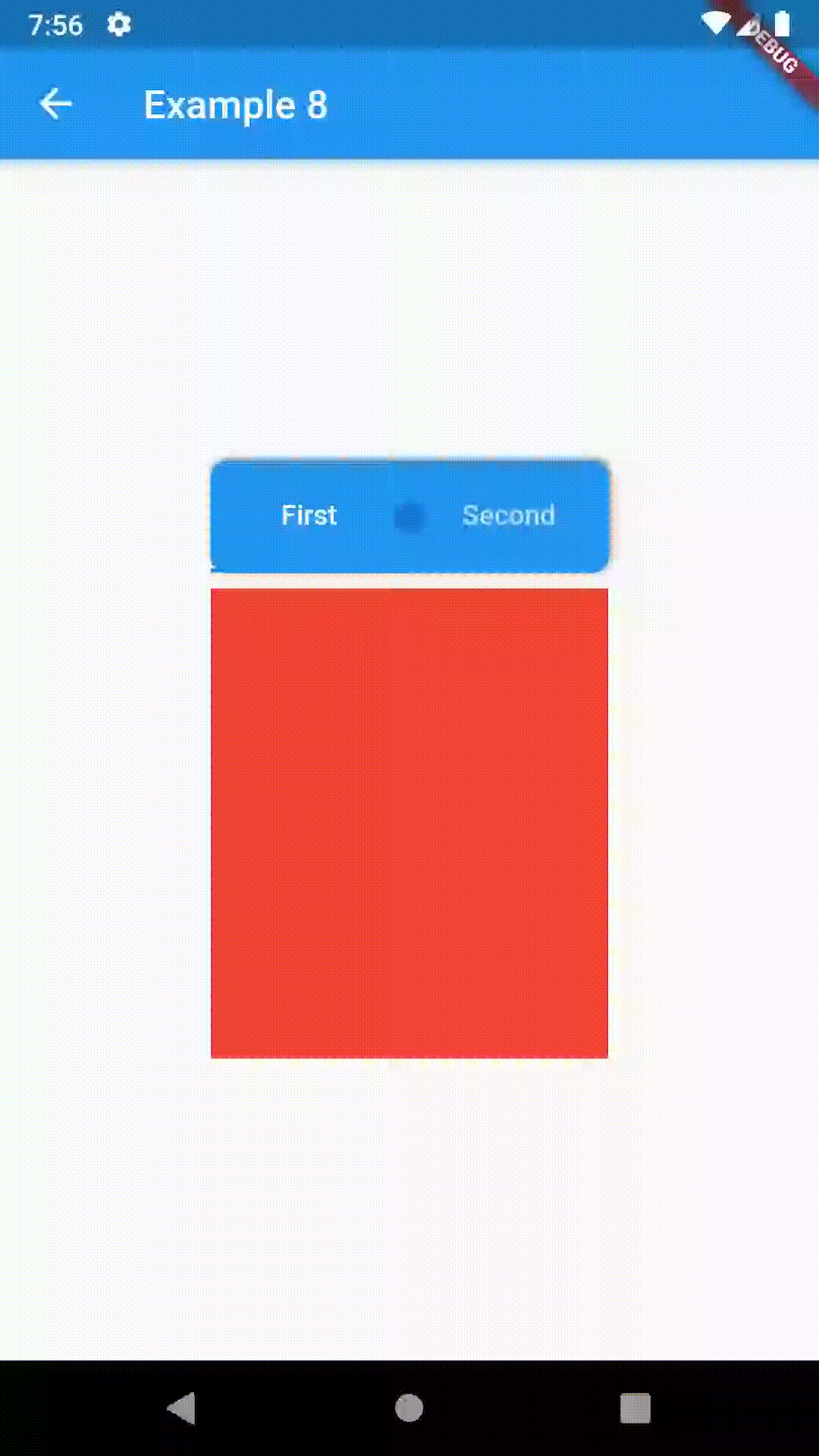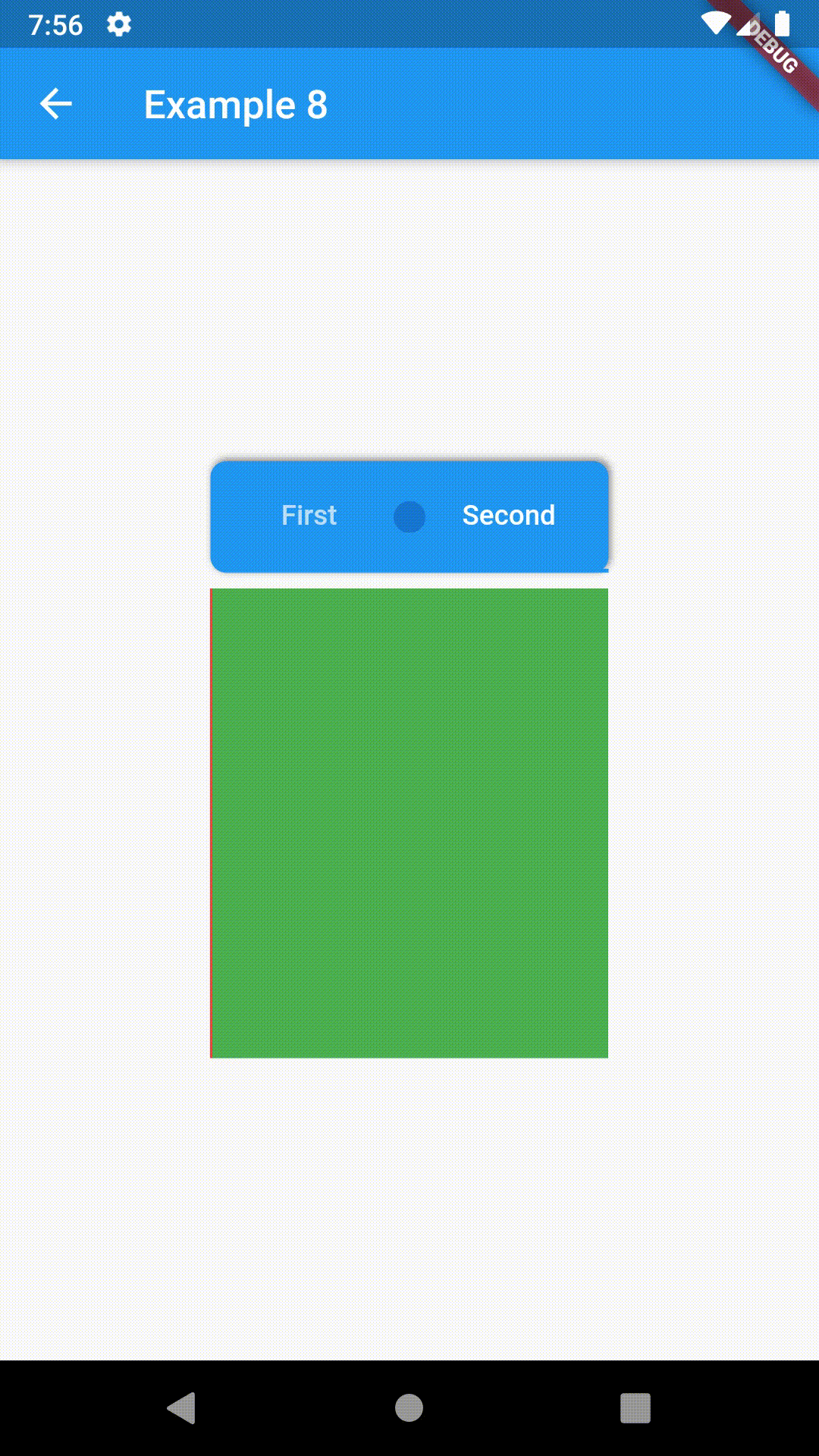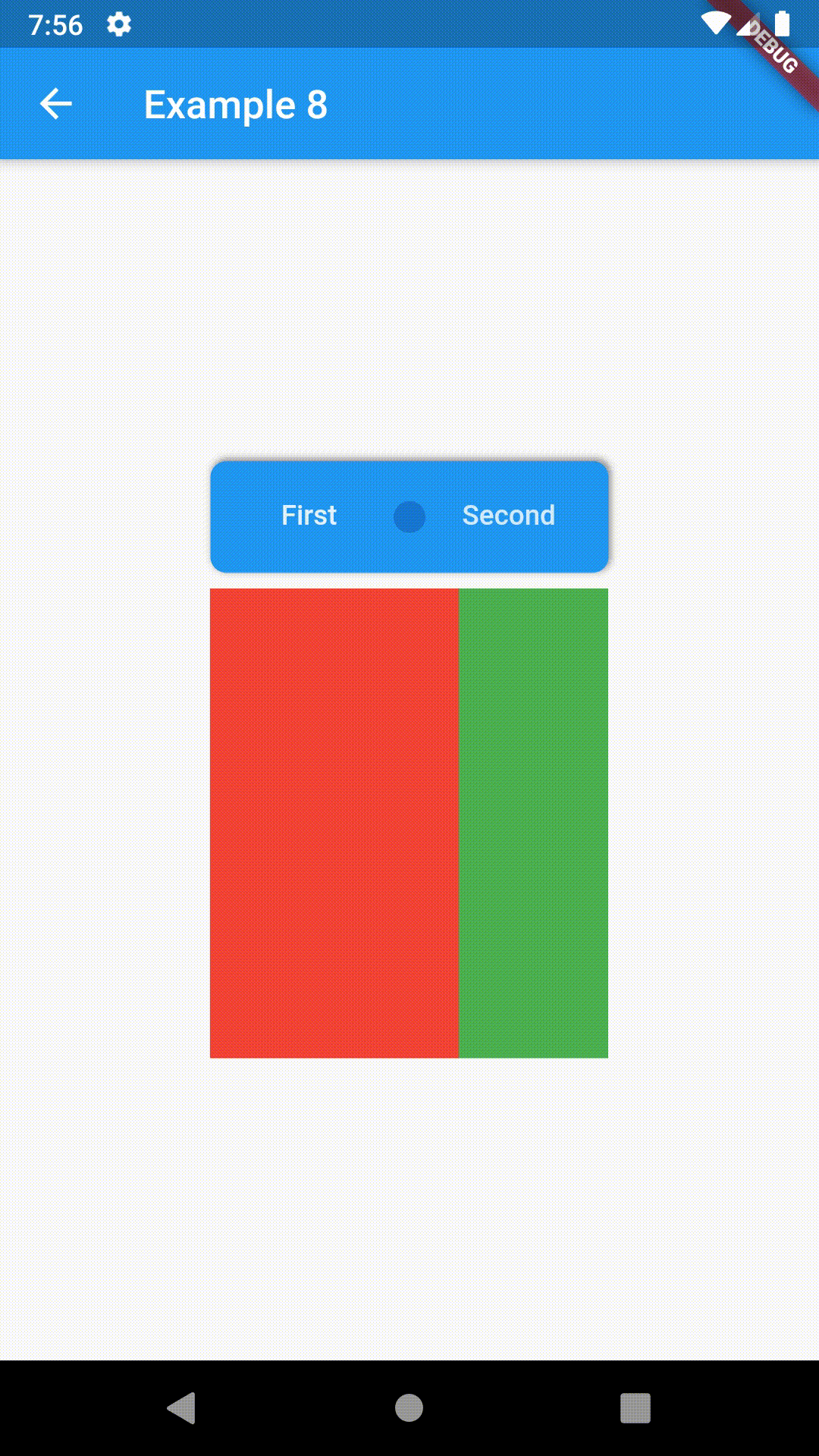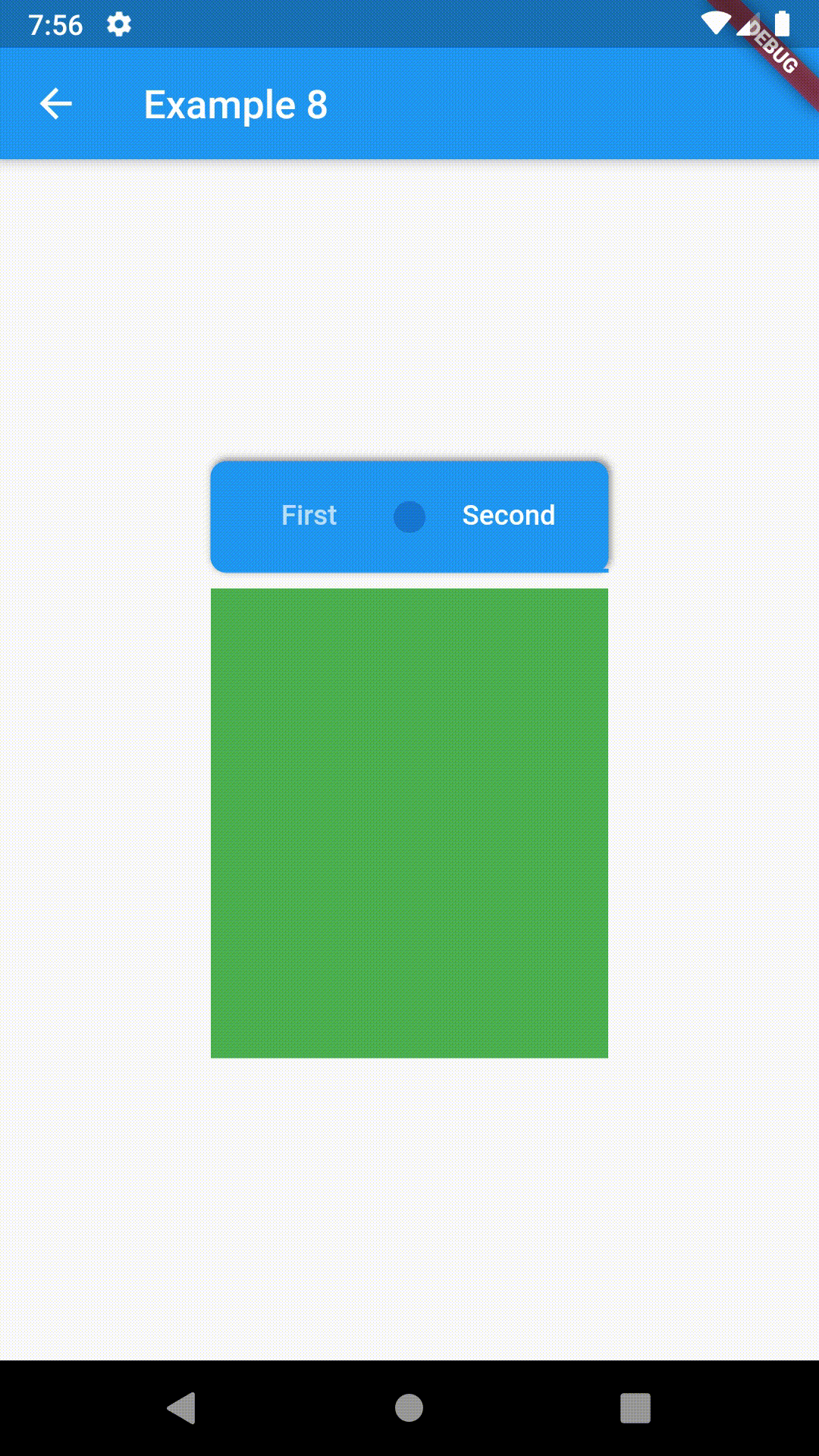
child: ContainedTabBarView(
tabs: [
Text('First'),
Text('Second')
],
views: [
Container(color: Colors.red),
Container(color: Colors.green)
],
onChange: (index) => print(index),
),
)
Intermediate #
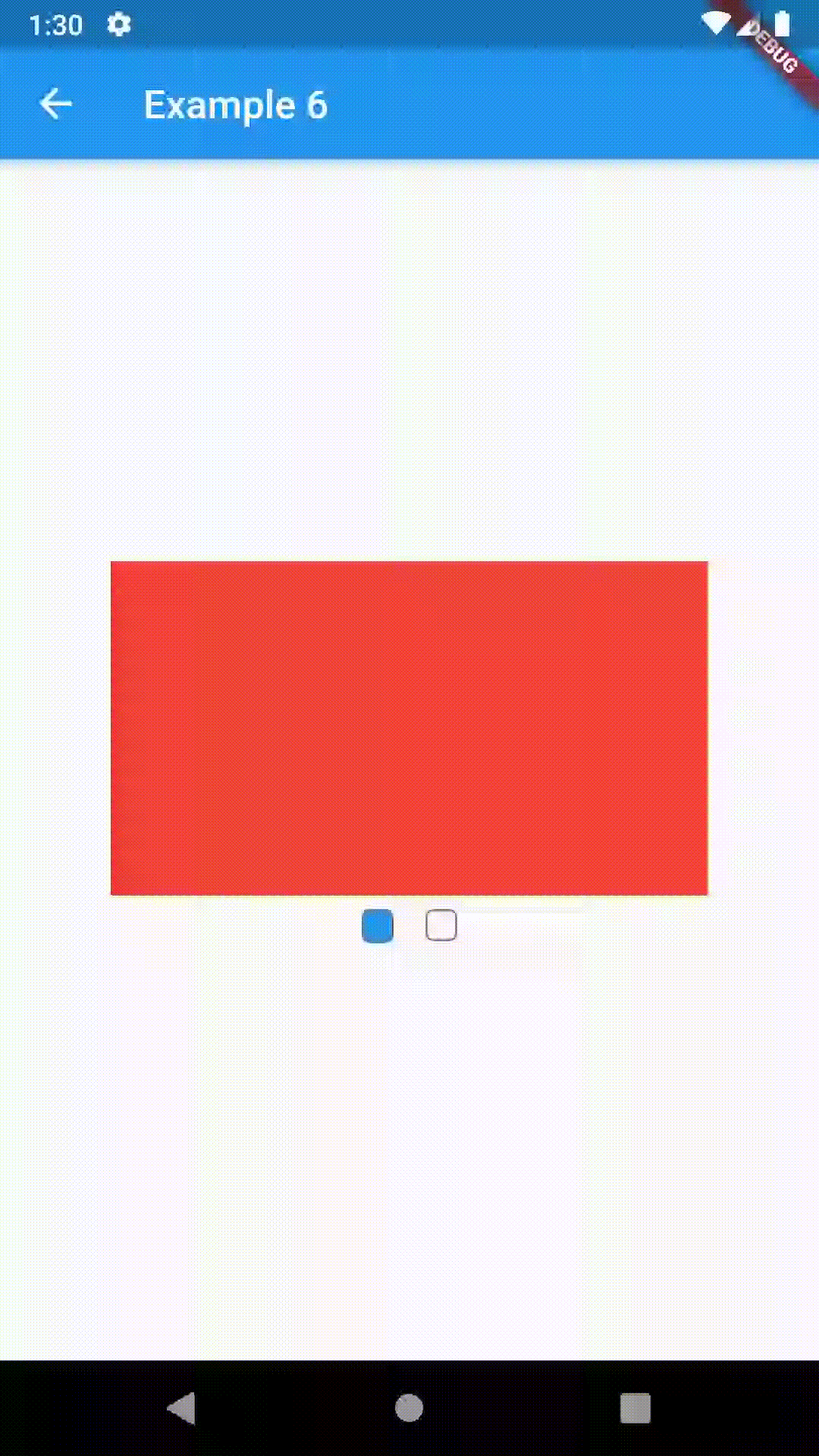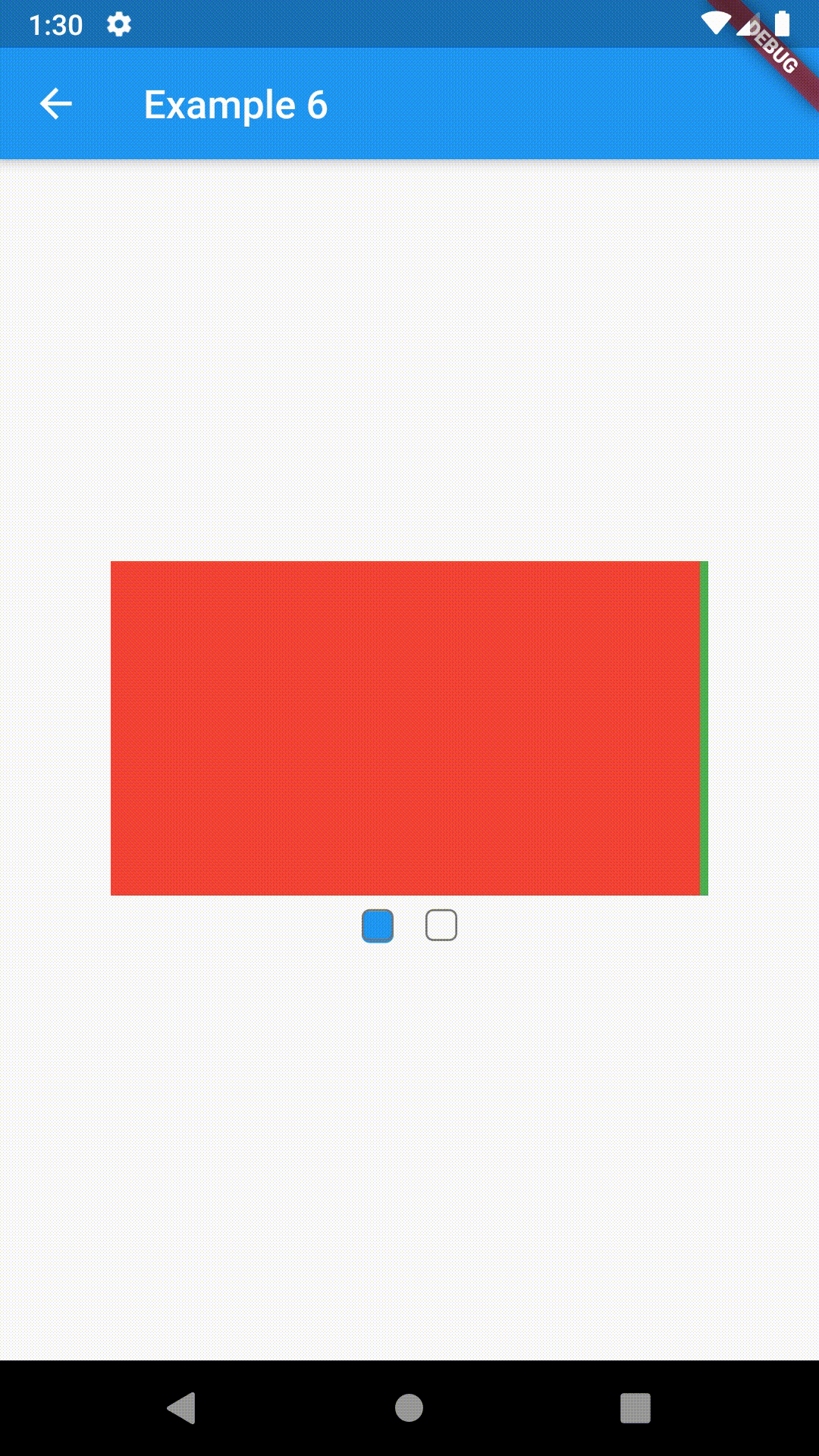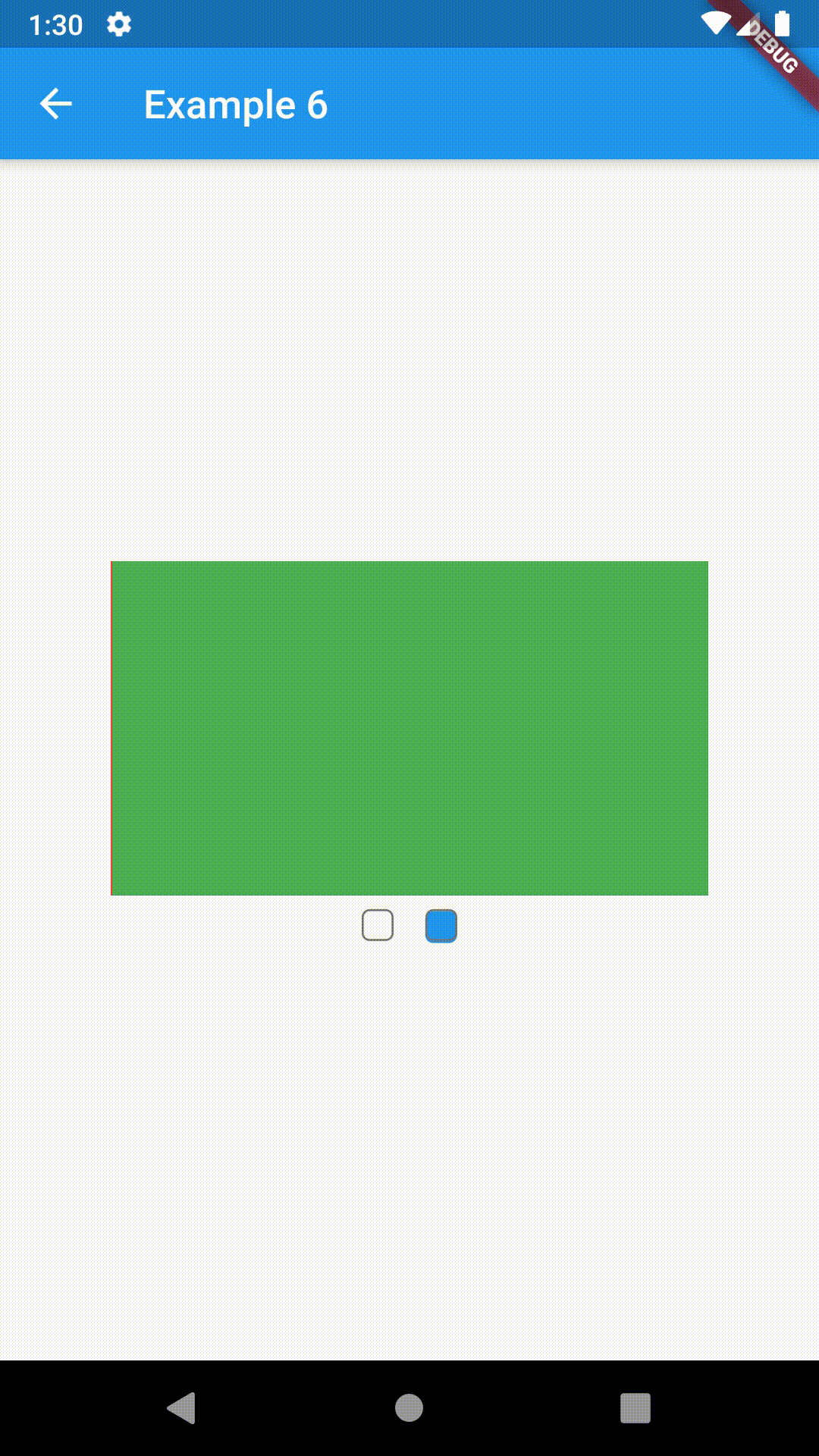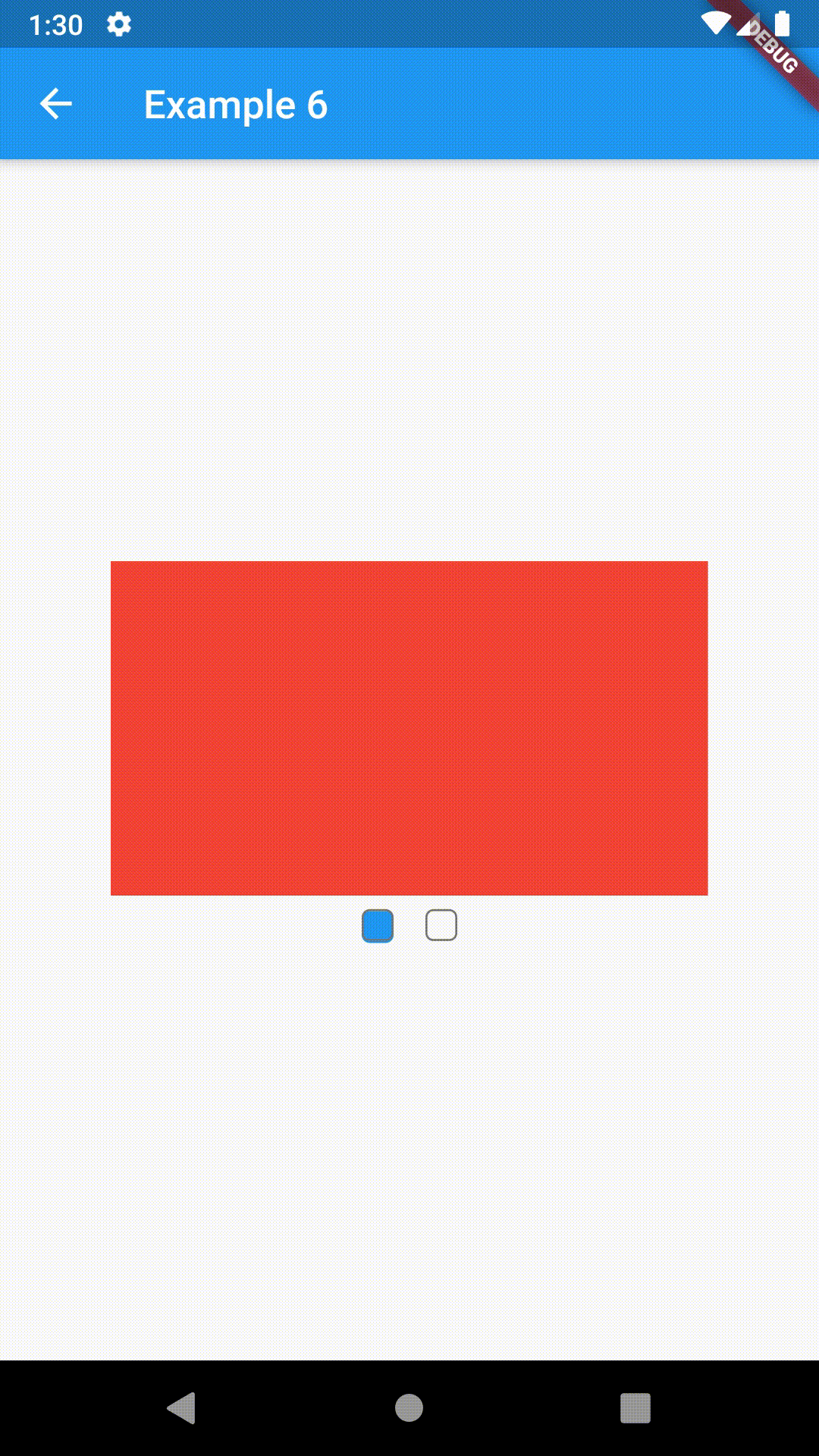
All the properties that can be set for a TabBar are accessible for setting via tabBarProperties. Also, there are many more for the customization of TabBar's appearance. To create your own ("container-based") indicator, you can use ContainerIndicator decoration (see examples 4 and 6).
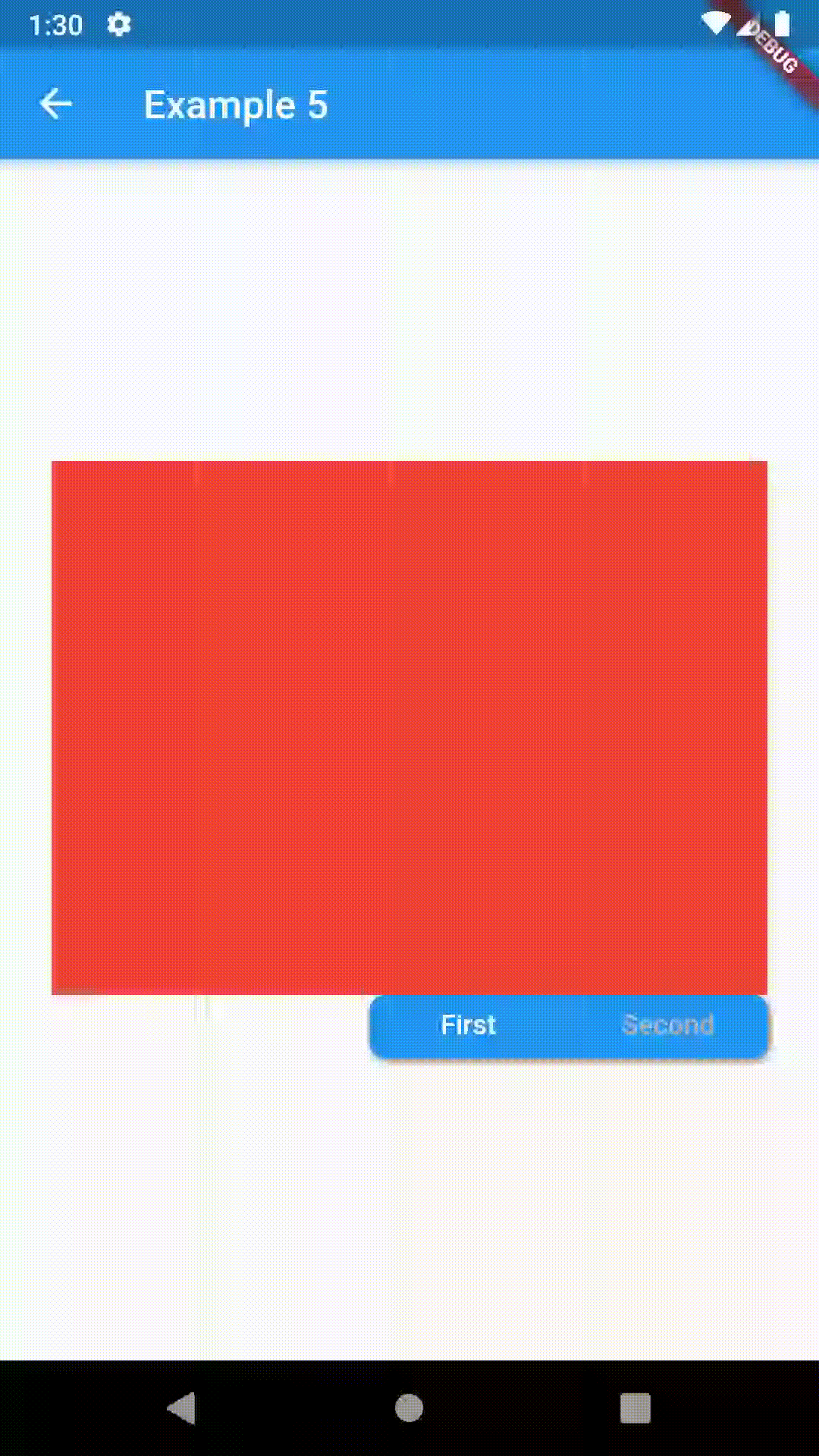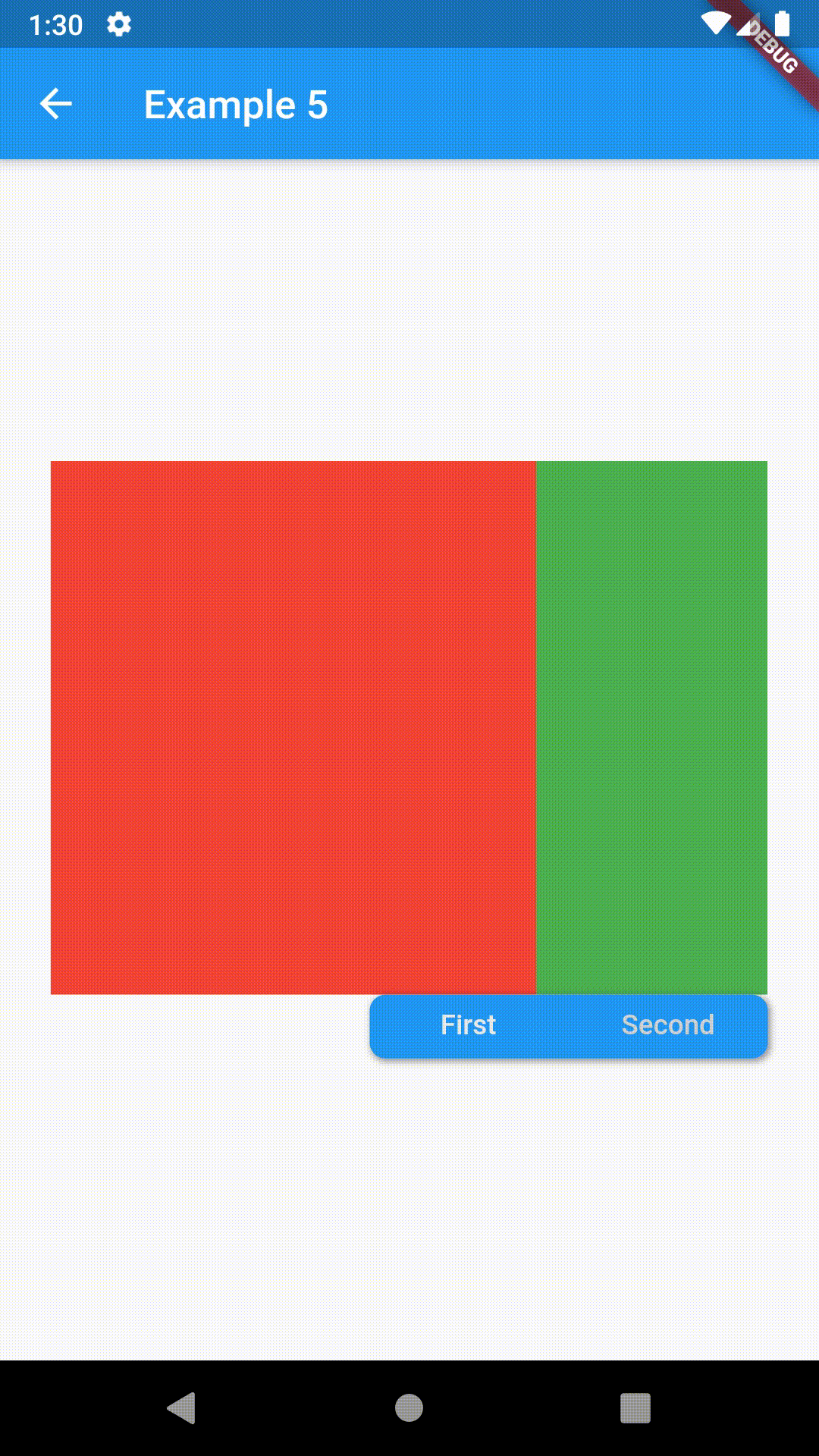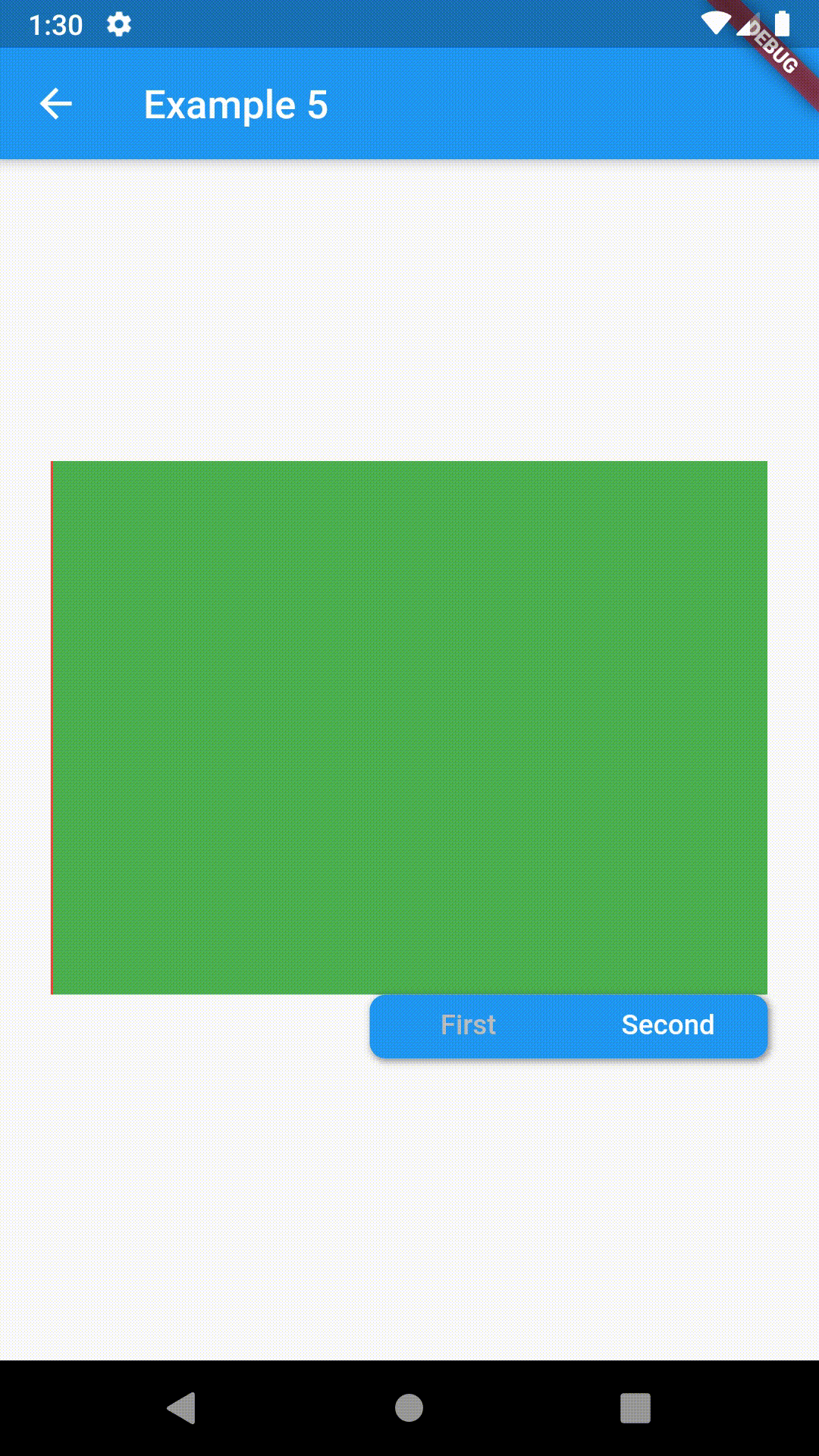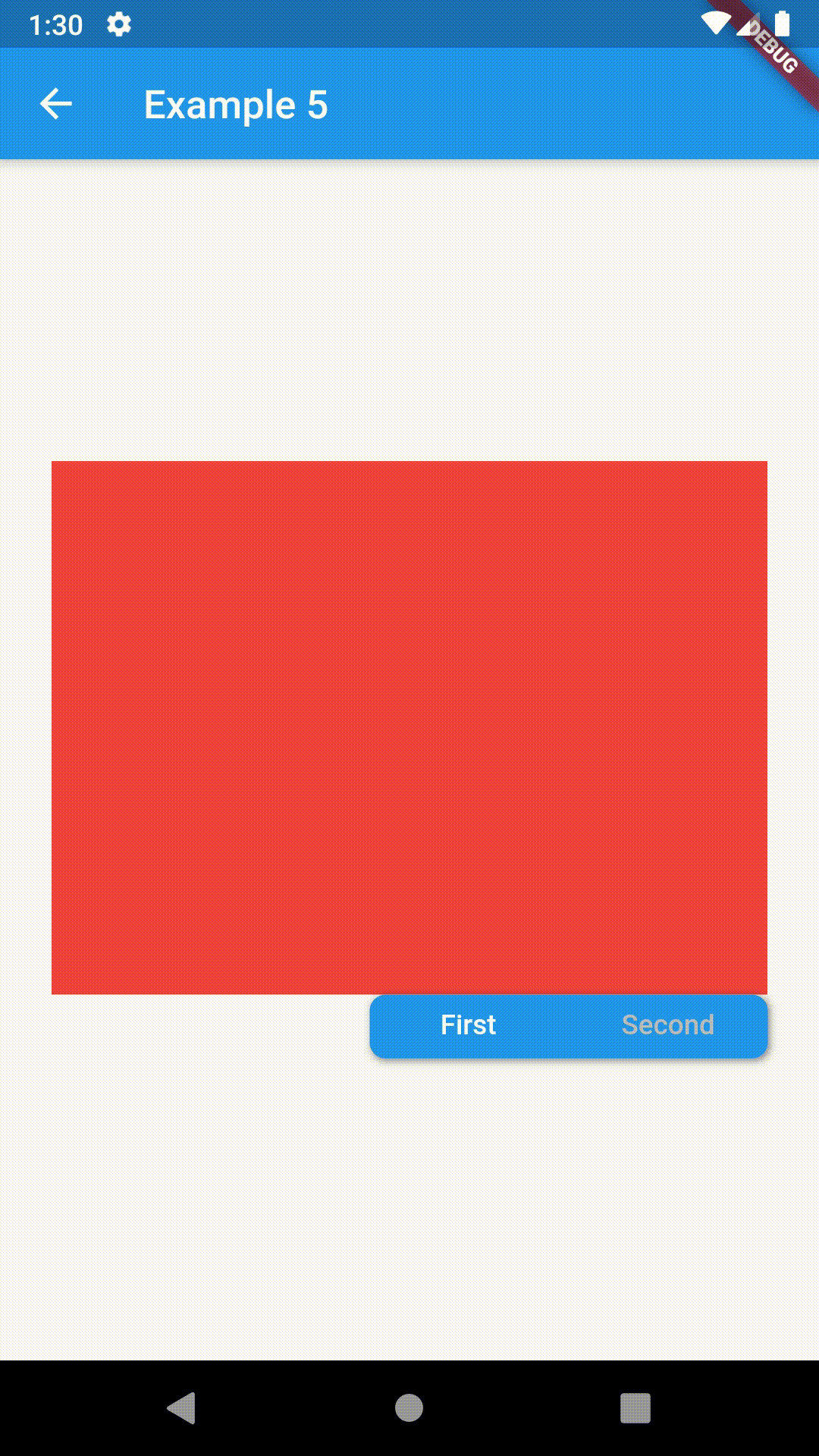
// Example 5
ContainedTabBarView(
tabs: [Text('First'), Text('Second')],
tabBarProperties: TabBarProperties(
width: 200,
height: 32,
position: TabBarPosition.bottom,
alignment: TabBarAlignment.end,
backgroundStack: Stack(
children: [
Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.blue,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.all(
Radius.circular(8.0)
),
boxShadow: [
BoxShadow(
color: Colors.black.withOpacity(0.4),
spreadRadius: 0.5,
blurRadius: 2,
offset: Offset(1, -1),
),
],
),
),
],
),
indicatorColor: Colors.transparent,
labelColor: Colors.white,
unselectedLabelColor: Colors.grey[400],
),
views: [
Container(color: Colors.red),
Container(color: Colors.green)
],
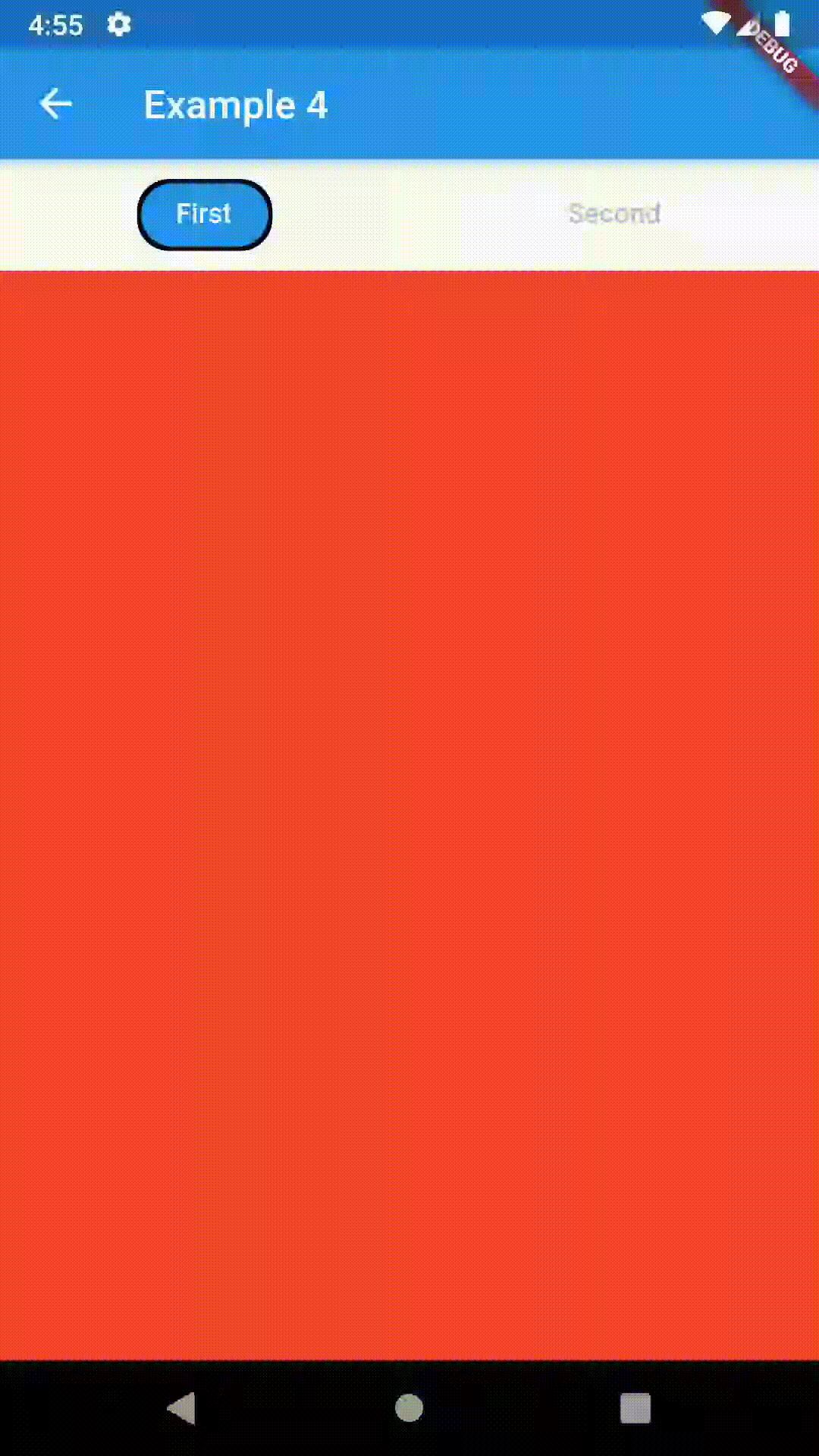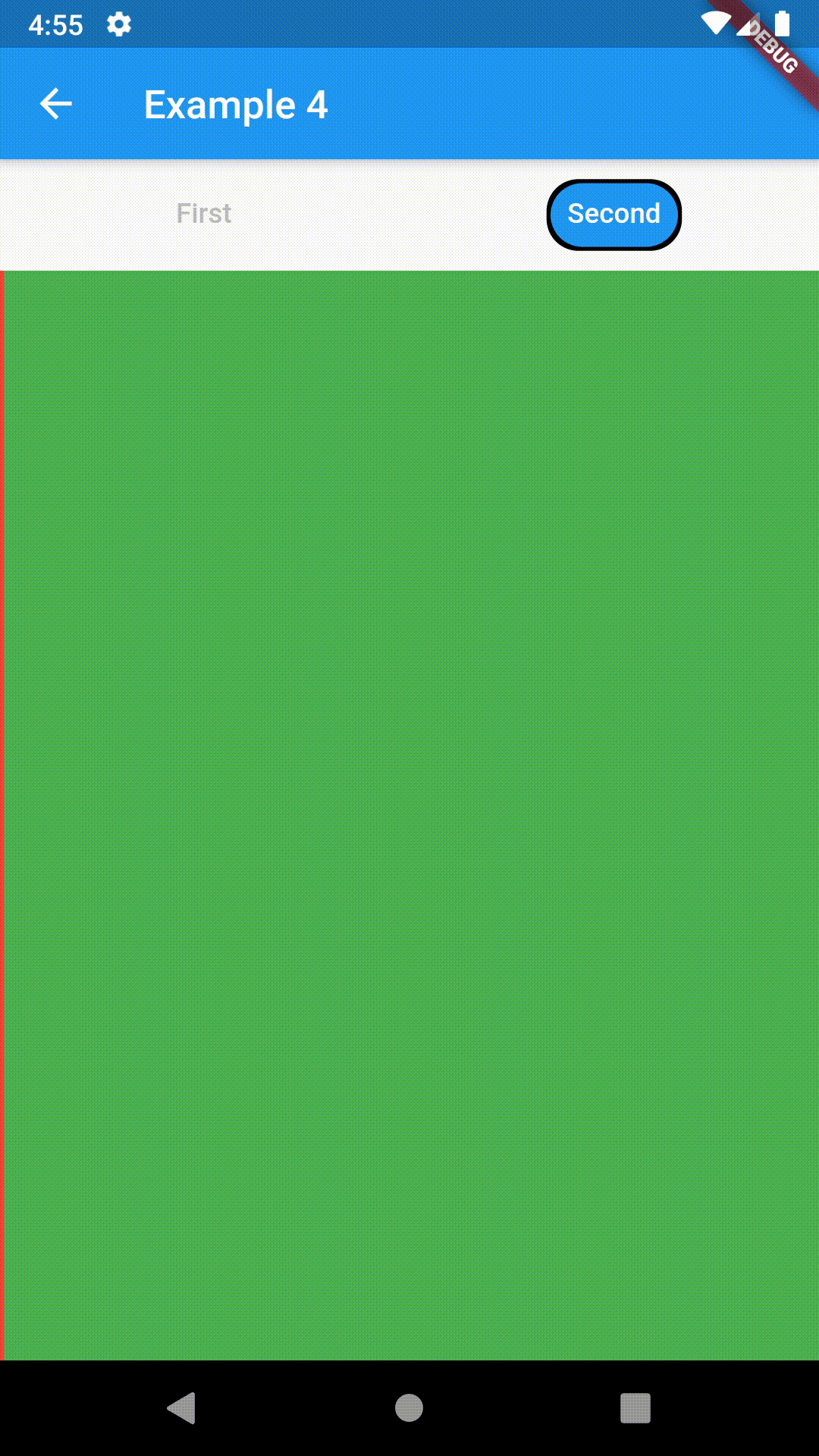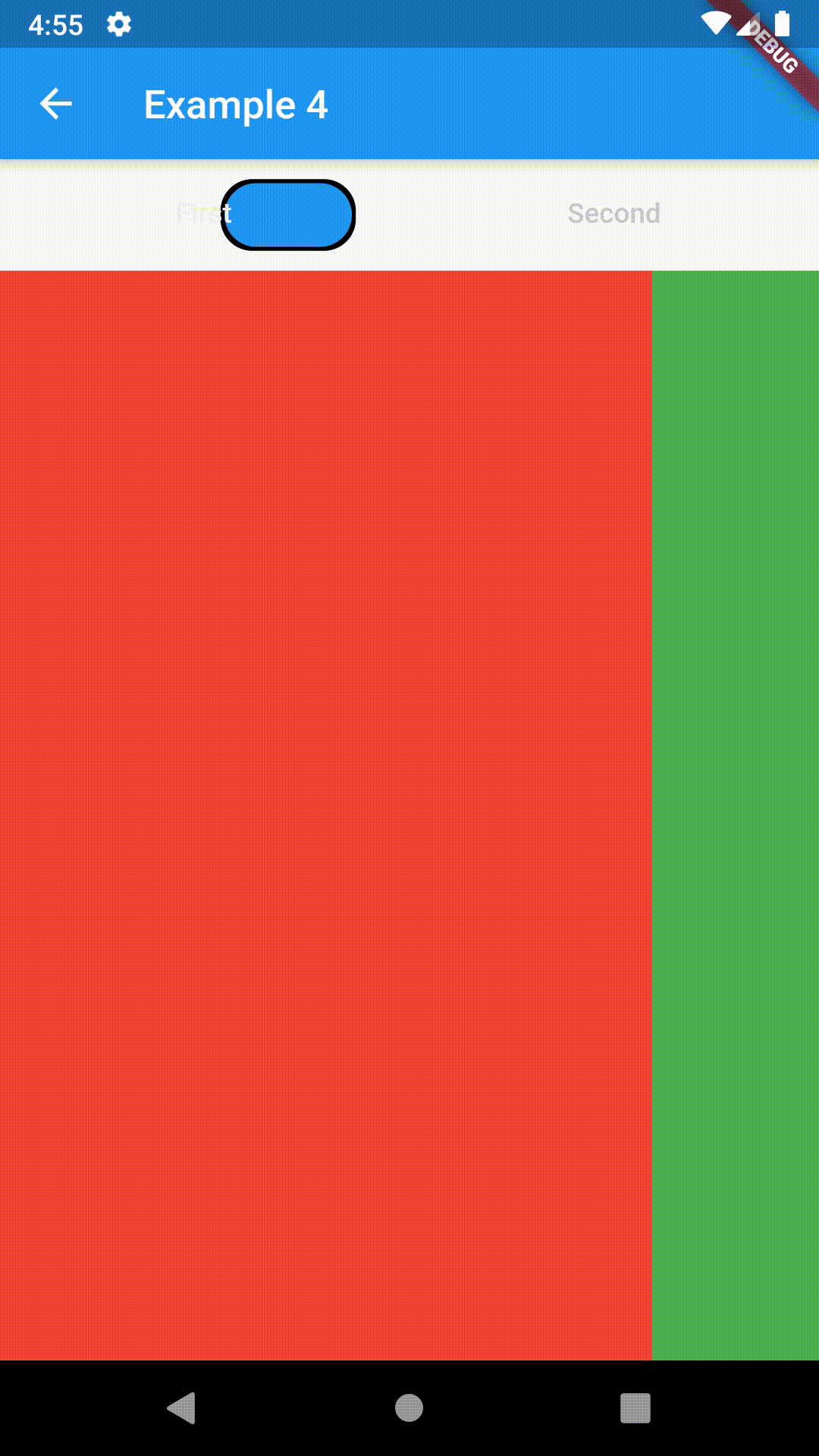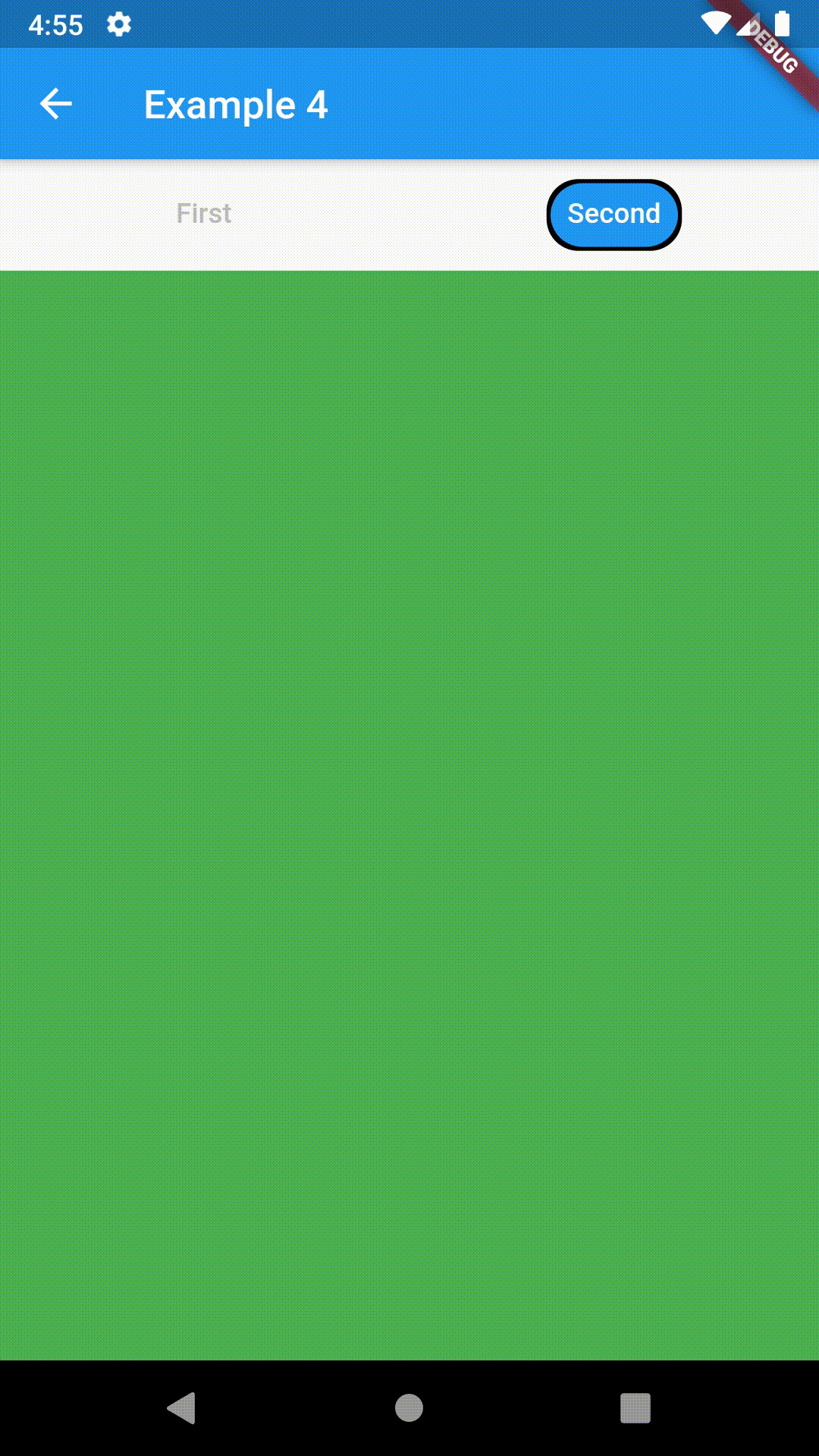
Advanced #
To control the state, i.e. move to another tab, from outside of ContainedTabBarView create it with a GlobalKey and then use methods exposed from state; animateTo(), next() and previous().
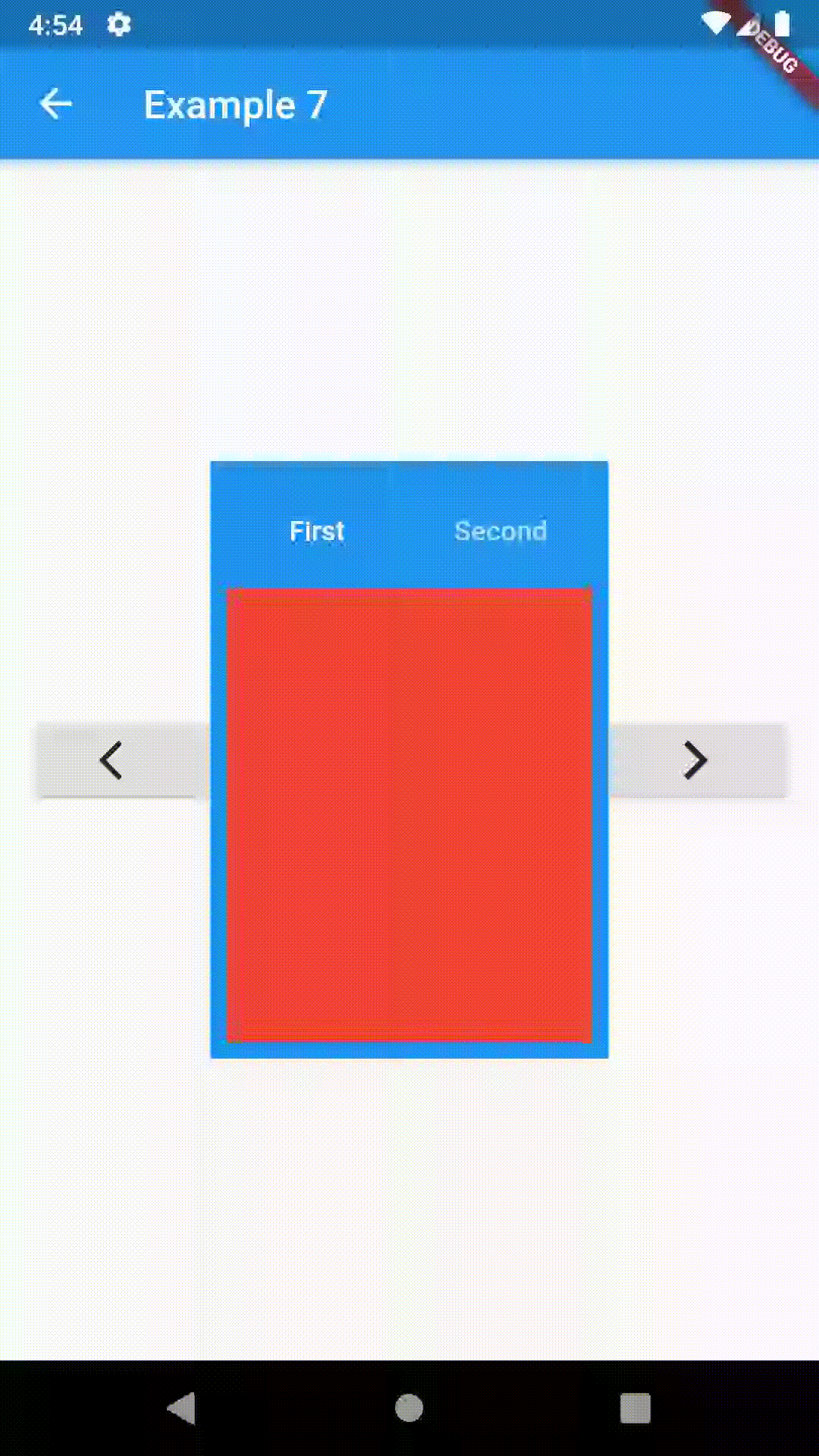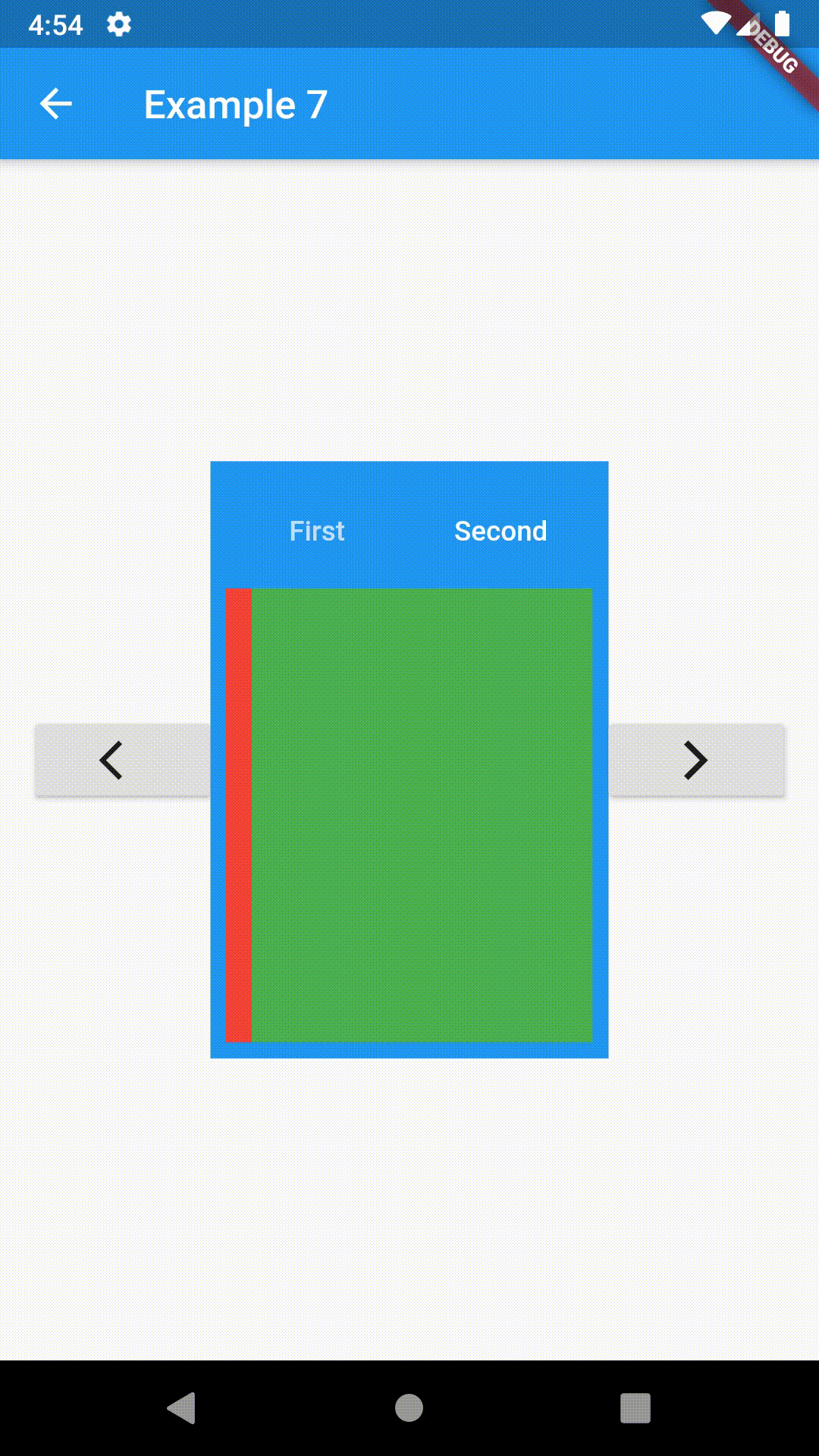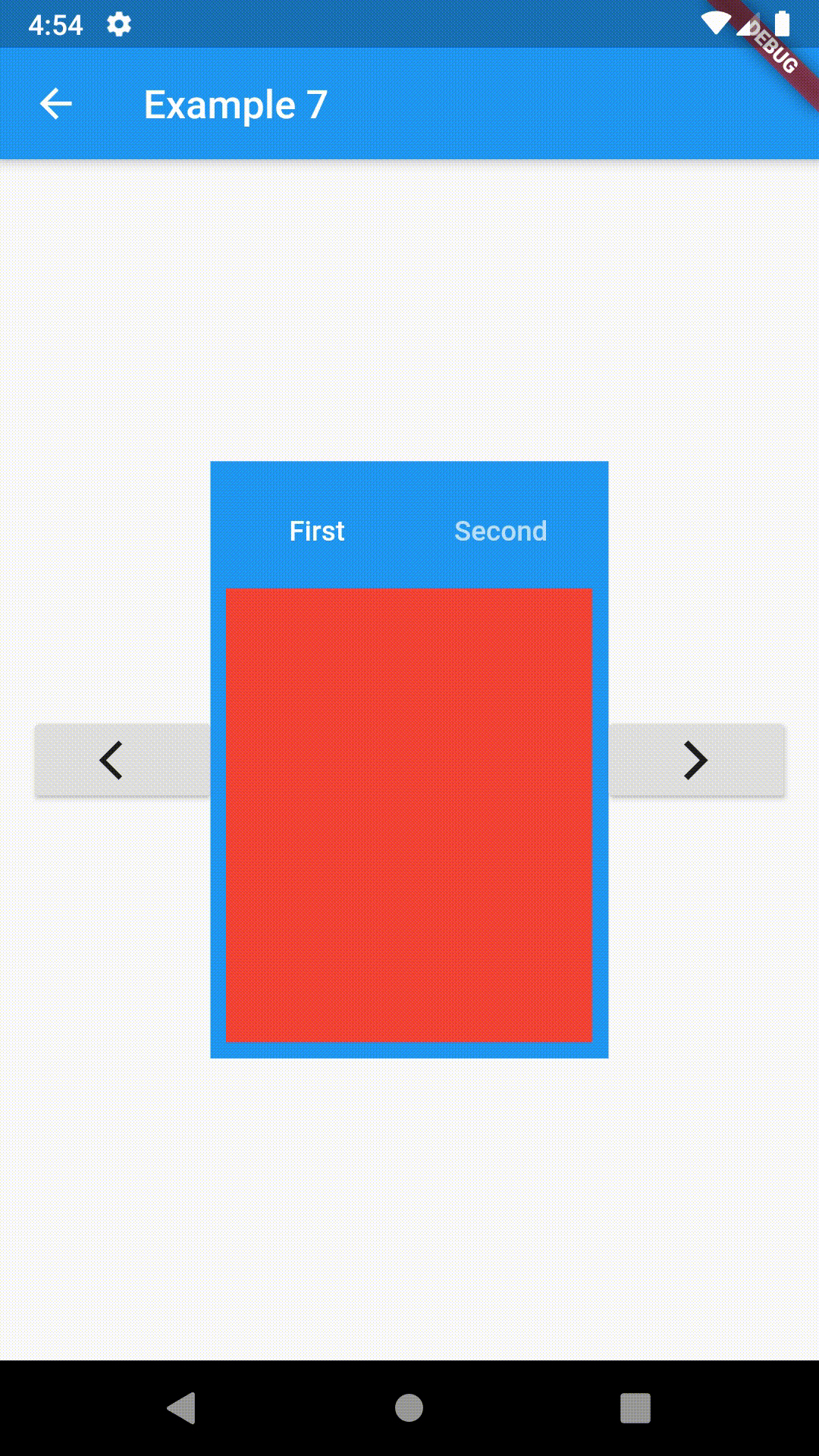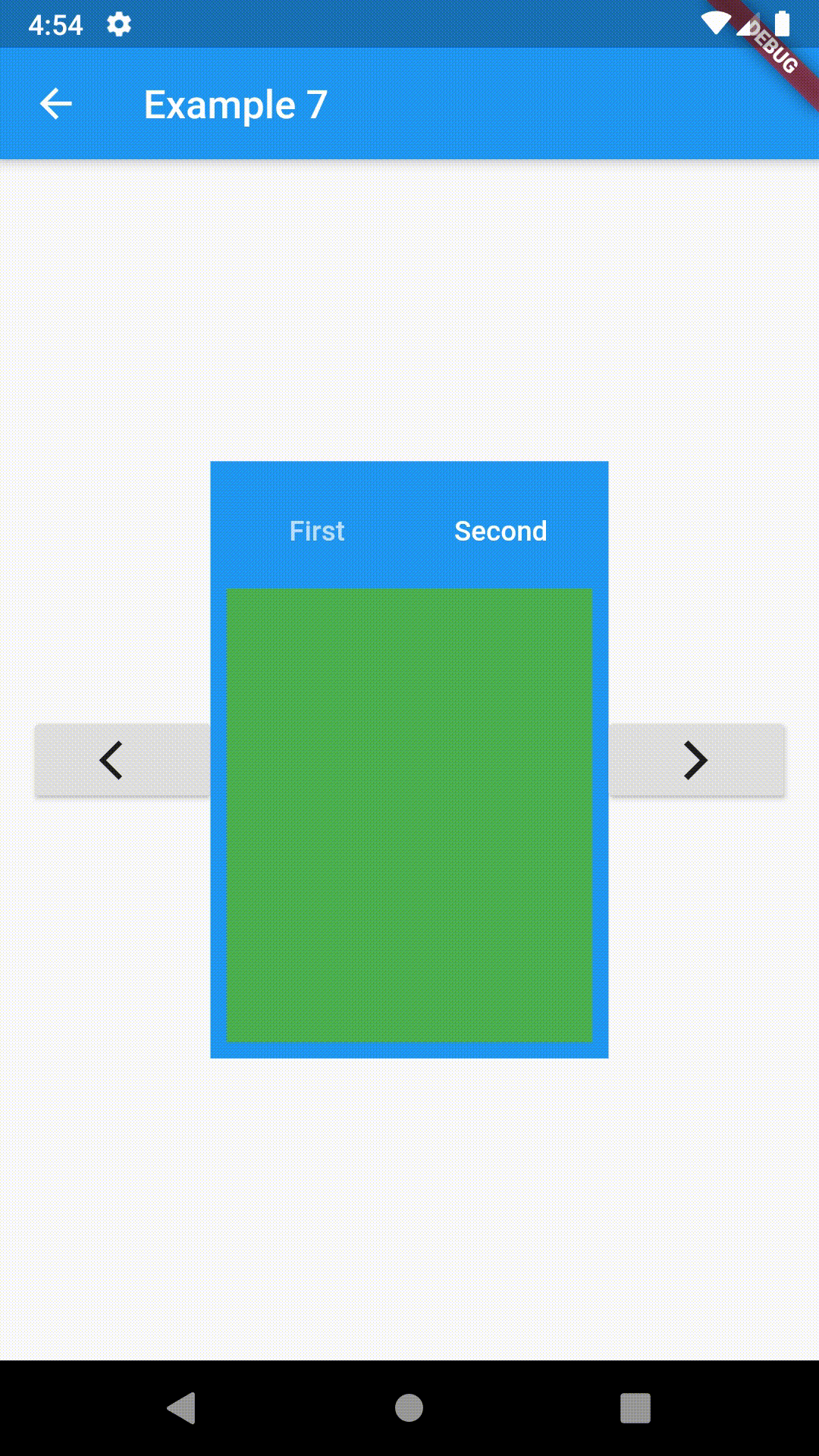
// Example 7
class Example7 extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
GlobalKey<ContainedTabBarViewState> _key = GlobalKey();
ContainedTabBarView containedTabBarView = ContainedTabBarView(
key: _key,
tabs: [
Text('First'),
Text('Second')
],
views: [
Container(color: Colors.red),
Container(color: Colors.green)
],
);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Example 7'),
),
body: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
RaisedButton(
child: Icon(Icons.arrow_back_ios),
onPressed: () => _key.currentState.previous(),
),
Center(
child: Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
color: Colors.blue,
width: 200,
height: 300,
child: containedTabBarView,
)),
RaisedButton(
child: Icon(Icons.arrow_forward_ios),
onPressed: () => _key.currentState.next(),
),
]
),
);
}
}