event_bus 0.2.2  event_bus: ^0.2.2 copied to clipboard
event_bus: ^0.2.2 copied to clipboard
A simple Event Bus using Dart Streams for decoupling applications
Event Bus #
A simple Event Bus using Dart Streams for decoupling applications.
Demo #
All examples are also available in the example directory on GitHub.
Event Bus Pattern #
An Event Bus follows the publish/subscribe pattern. It allows listeners to subscribe for events and publishers to fire events. This enables objects to interact without requiring to explicitly define listeners and keeping track of them.
Event Bus and MVC #
The Event Bus pattern is especially helpful for decoupling MVC (or MVP) applications.
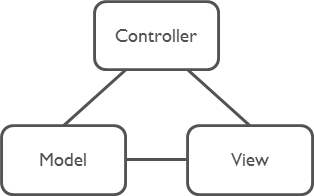
One group of MVC is not a problem.
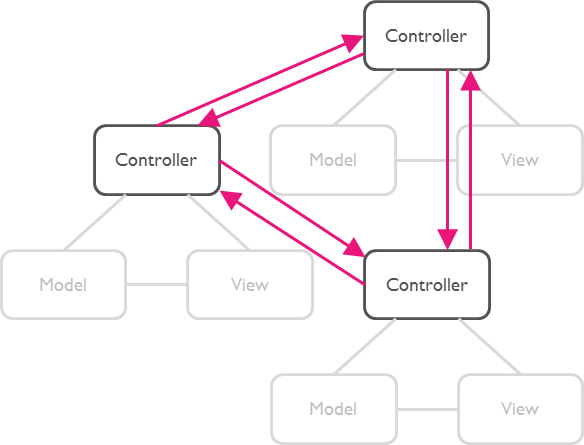
But as soon as there are multiple groups of MVCs, those groups will have to talk to each other. This creates a tight coupling between the controllers.
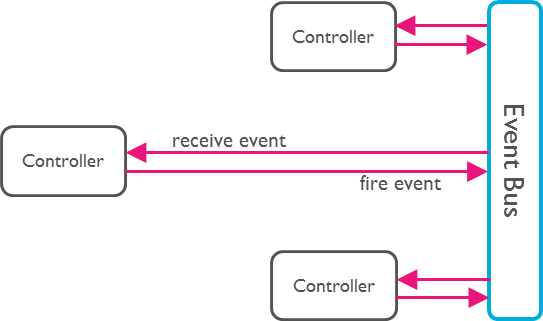
By communication through an Event Bus, the coupling is reduced.
Usage #
1. Add Dependency #
Add the folowing to your pubspec.yaml and run pub install
dependencies:
event_bus: any
2. Define Events #
import 'package:event_bus/event_bus.dart';
final EventType<User> userLoggedInEvent = new EventType<User>();
final EventType<Order> newOrderEvent = new EventType<Order>();
Note: The generic type of the event (User and Order in this case) is the
type of data that will be provided when the event is fired.
3. Create Event Bus #
Create an instance of EventBus and make it available to other classes.
Usually there is just one Event Bus per application, but more than one may be set up to group a specific set of events.
EventBus eventBus = new EventBus();
This will instantiate the default implementation of EventBus which is
SimpleEventBus. You may provide your own EventBus by either extending
SimpleEventBus or implementing EventBus.
4. Register Listeners #
Register listeners that will be called whenever the event is fired.
eventBus.on(userLoggedInEvent).listen((User user) {
print(user.name);
});
EventBus uses Dart Streams
as its underlying mechanism to keep track of listeners. You may use all
functionality available by the Stream
API. One example is the use of StreamSubscriptions
to later unsubscribe from the events.
StreamSubscription<User> subscription = eventBus.on(userLoggedInEvent).listen((User user) {
print(user.name);
});
subscription.cancel();
5. Fire Events #
Finally, we need to fire an event.
eventBus.fire(userLoggedInEvent, new User('Mickey'));
License #
The MIT License (MIT)