flutter_media_store 1.3.1  flutter_media_store: ^1.3.1 copied to clipboard
flutter_media_store: ^1.3.1 copied to clipboard
A Flutter plugin to save, append data and pick files in Android MediaStore seamlessly.
Flutter Media Store Plugin #
Welcome to the Flutter Media Store Plugin! This plugin allows you to save and pick various types of files (images, videos, audio, documents, etc.) directly to/from the device's Android MediaStore, enabling seamless integration with Android's storage system. It supports all Android versions.
With this plugin, you can:
- Save files with data (images, videos, audio, documents, etc.).
- Insert new data into existing files.
- Pick files from the MediaStore.
Features #
- Save files to MediaStore: Easily save files such as images, audio, video, CSV, text, and more.
- Append data to existing files: Allows appending data to files already saved in MediaStore (e.g., adding additional content to existing files).
- Pick files from MediaStore: Pick files from the device's storage (images, videos, audio, and other documents) securely.
- Android-specific: This plugin currently supports Android devices.
- Automatic Permission Handling: The plugin checks and requests storage permissions to ensure proper functionality.
- Cross-file type support: Save different file types like PNG, JPG, PDF, CSV, TXT, XML, Json, MP3, MP4, ZIP, Tar, etc.
Scoped Storage and MediaStore #
Scoped Storage #
Introduced in Android 10 (API 29), Scoped Storage enhances privacy by restricting apps' access to files. Apps can only access private storage and designated public directories (e.g., photos, videos). This prevents access to sensitive system or other apps' private data.
MediaStore #
MediaStore allows secure interaction with media files (images, audio, videos) on Android devices, adhering to Scoped Storage rules. Apps can read/write media files in structured, secure collections without accessing arbitrary file locations.
Flutter Media Store Plugin #
The Flutter Media Store Plugin integrates seamlessly with Scoped Storage and MediaStore, enabling compliant and secure file management.
Benefits:
- Automatic Permissions: Handles storage permissions efficiently.
- Multi-File Type Support: Save and retrieve images, audio, video, and documents in MediaStore.
- Scoped Storage Compliance: Ensures secure, structured file access aligned with Android's privacy policies.
This plugin simplifies file management while adhering to modern Android storage standards.
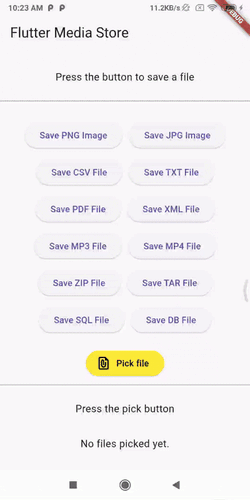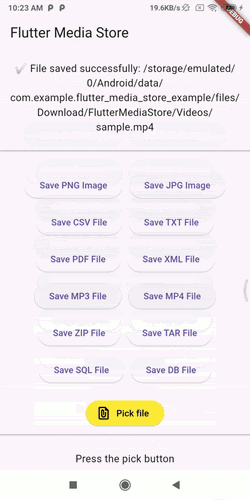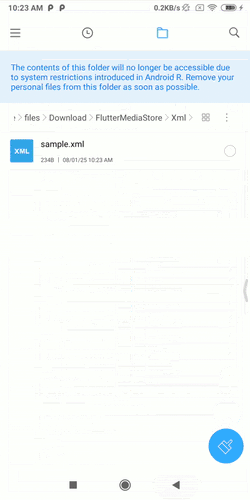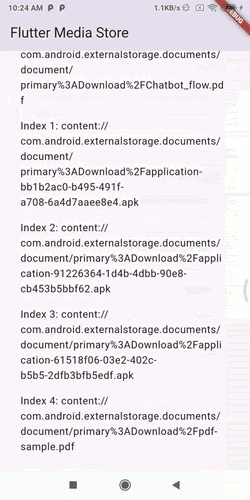
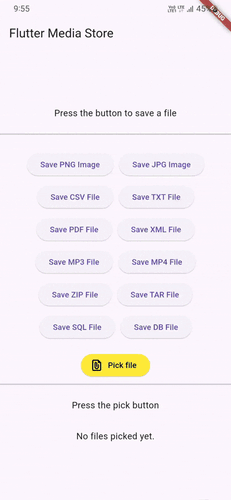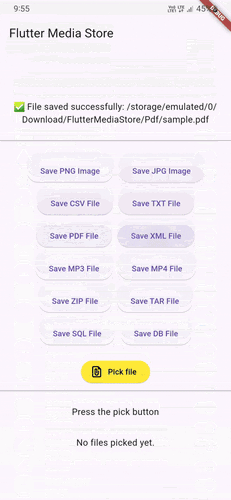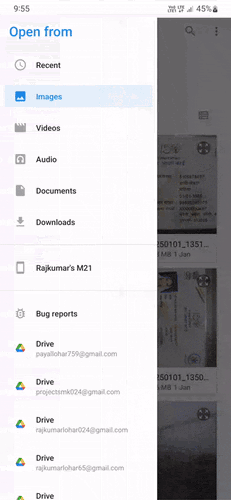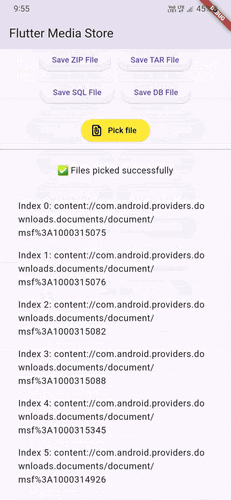
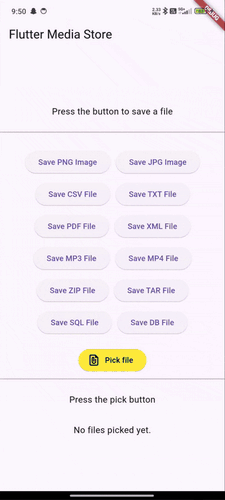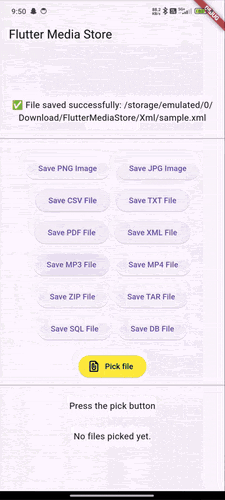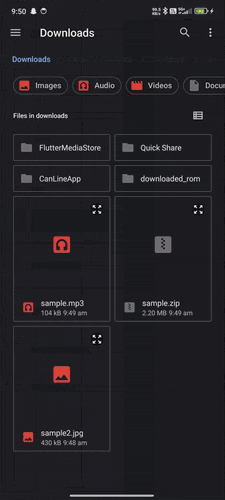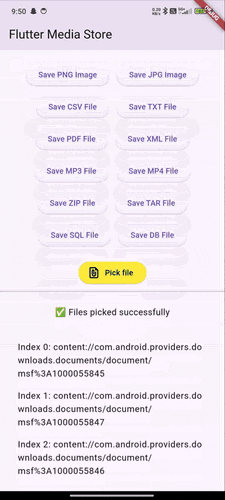
Demo GIFs #
Watch these demo GIFs to see the plugin in action on various Android versions:
| Android 9 | Android 12 | Android 14 |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
Installation #
To get started with the Flutter Media Store Plugin, follow these steps:
-
Add the dependency to your
pubspec.yamlfile:dependencies: flutter: sdk: flutter flutter_media_store: ^1.3.1 -
Run
flutter pub getto fetch the plugin and its dependencies. -
Android Permissions: For the plugin to work, you need to add the necessary permissions to your Android app:
In
android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml, add the following lines:<!-- Permission to read files from external storage (Required for API level <= 29) --> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" android:maxSdkVersion="29" /> <!-- Permission to write files to external storage (Required for API level <= 29, deprecated in API level 30 and above. Use MANAGE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE for API >= 30) --> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" android:maxSdkVersion="29" /> <!-- Permission to manage all files on external storage (Required for API level >= 30, covers reading and writing) --> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MANAGE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" /> -
Handling Permissions: The plugin automatically requests permission to access the device storage. If permission is denied, it displays a message to the user prompting them to grant permission.
Usage #
Once the plugin is installed and permissions are configured, you can start saving files to the device's MediaStore.
Example Code #
The main methods to save a file are saveFile and appendDataToFile. Here's an example of how to use them:
Future<void> saveAppendMethod({
required String assetPath,
required String mimeType,
required String fileName,
required String rootFolderName,
required String folderName,
}) async {
final flutterMediaStorePlugin = FlutterMediaStore();
try {
// Load file from assets using rootBundle
ByteData byteData = await rootBundle.load(assetPath);
Uint8List fileData = byteData.buffer.asUint8List();
// Save the file using the plugin and handle success/error via callbacks
await flutterMediaStorePlugin.saveFile(
fileData: fileData, // **saveFile** saves the file with data and returns a URI
mimeType: mimeType,
rootFolderName: rootFolderName,
folderName: folderName,
fileName: fileName,
onSuccess: (String uri, String filePath) {
// Callbacks on success
print('✅ File saved successfully: $filePath.toString()');
print('uri: ${uri.toString()}');
// **appendDataToFile** is used to append new data to the existing file using the returned URI
flutterMediaStorePlugin.appendDataToFile(
uri: uri, // append new data using the URI returned by saveFile
fileData: fileData, // append new data
onSuccess: (result) {
print(result);
},
onError: (errorMessage) {
print(errorMessage);
},
);
},
onError: (String errorMessage) {
// Callbacks on error
print('❌ Failed to save file: $errorMessage');
},
);
} catch (e) {
// Catch and log any errors that may occur during the process
print('❌ Error loading file from assets: ${e.toString()}');
}
}
Explanation #
-
Convert Data to Bytes:
Before saving or appending data, you must convert the data (e.g., an image, video, audio, etc.) to bytes. In this example, therootBundle.load(assetPath)method loads the file from assets, and then theByteDatais converted toUint8List(bytes) usingbyteData.buffer.asUint8List(). This byte array is then passed tosaveFileorappendDataToFile. -
saveFile:
This method saves a file with the data in byte format and returns a URI that identifies the saved file in the MediaStore. -
appendDataToFile:
This method appends new data to an existing file. The new data is passed as bytes, and the method uses the URI from thesaveFilemethod to target the file for appending.
To pick a file, you can use the pickFile method. Here's how you can use it: #
FlutterMediaStore().pickFile(
multipleSelect: true,
onFilesPicked: (List<String> uris) {
print('✅ Files picked successfully');
// Loop through the list and print each URI
uris.forEach((uri) {
print('Picked file URI: $uri');
});
},
onError: (String error) {
print('❌ Failed to pick file');
},
);
Explanation: #
- pickFile: This method allows users to pick a file from their Android device's MediaStore (e.g., image, audio, video, etc.). It returns the file path once the user selects a file.
Single Select vs. Multi-Select: #
- Single Select: When
multipleSelectis set tofalse(default), only one file can be selected. - Multi-Select: When
multipleSelectis set totrue, users can select multiple files at once.
MIME Type List #
MIME types (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) are used to specify the type of content or file format. It helps applications and services understand the type of file they are handling and ensures the correct handling and processing of files.
Below is a list of supported MIME types for different file types:
PNG Image: image/png
JPG Image: image/jpeg
PDF File: application/pdf
CSV File: text/csv
TXT File: text/plain
XML File: application/xml
JSON File: application/json
MP3 File: audio/mpeg
MP4 Video: video/mp4
ZIP Archive: application/zip
TAR Archive: application/x-tar
DB File: application/octet-stream
You can also use other MIME types depending on the file format you are working with. Simply provide the appropriate MIME type for the content to ensure proper handling and compatibility.
MIME Use Example #
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () => saveFile(
assetPath: 'assets/img/sample1.png',
mimeType: 'image/png',
fileName: 'sample1',
folderName: 'Images/png',
rootFolderName: rootFolderName,
),
child: const Text('Save PNG Image'),
)
Why Use URIs? #
URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) is a string that identifies a resource either by location, name, or both. In Android, URIs are widely used to access and manage files stored on the device or within apps.
Benefits of Using URIs: #
- Unified Resource Access: URIs allow access to files across different storage mechanisms (internal, external, MediaStore, etc.) without needing absolute file paths.
- Scoped Storage Compliance: Using URIs ensures compliance with Android's Scoped Storage policies, introduced in Android 10, enhancing security and privacy.
- Simplifies File Management: Enables direct interaction with resources like images, videos, and documents via content providers without requiring manual file management.
- Cross-App Compatibility: URIs facilitate sharing and accessing files across apps using content providers.
By leveraging URIs in your application, you ensure robust and secure file handling while adhering to modern Android development standards.
License #
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
