reorderables 0.2.0  reorderables: ^0.2.0 copied to clipboard
reorderables: ^0.2.0 copied to clipboard
Reorderable table, row, column, wrap, sliver list that allow drag and drop of their children.
reorderables #
Various reorderable, a.k.a. drag and drop, Flutter widgets, including reorderable table, row, column, wrap, and sliver list, that make their children draggable and
reorder them within the widget. Parent widget only need to provide an onReorder function that is invoked with the old and new indexes of child being reordered.
Usage #
To use this package, add reorderables as a dependency in your pubspec.yaml file.
dependencies:
reorderables:
And import the package in your code.
import 'package:reorderables/reorderables.dart';
Examples #
This package includes ReorderableSliverList, ReorderableTable, ReorderableWrap, ReorderableRow, and ReorderableColumn, which are reorderable versions of Flutter's SliverList, Table, Wrap, Row, and Column respectively.





ReorderableSliverList #
ReorderableSliverList behaves exactly like SliverList, but its children are draggable.
To make a SliverList reorderable, replace it with ReorderableSliverList and replace SliverChildListDelegate/SliverChildBuilderDelegate with ReorderableSliverChildListDelegate/ReorderableSliverChildBuilderDelegate.
class _SliverExampleState extends State<SliverExample> {
List<Widget> _rows;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_rows = List<Widget>.generate(50,
(int index) => Text('This is sliver child $index', key: ValueKey(index), textScaleFactor: 2)
);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
void _onReorder(int oldIndex, int newIndex) {
setState(() {
Widget row = _rows.removeAt(oldIndex);
_rows.insert(newIndex, row);
});
}
ScrollController _scrollController = PrimaryScrollController.of(context) ?? ScrollController();
return CustomScrollView(
// a ScrollController must be included in CustomScrollView, otherwise
// ReorderableSliverList wouldn't work
controller: _scrollController,
slivers: <Widget>[
SliverAppBar(
expandedHeight: 210.0,
flexibleSpace: FlexibleSpaceBar(
title: Text('ReorderableSliverList'),
background: Image.network(
'https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/68/Yushan'
'_main_east_peak%2BHuang_Chung_Yu%E9%BB%83%E4%B8%AD%E4%BD%91%2B'
'9030.png/640px-Yushan_main_east_peak%2BHuang_Chung_Yu%E9%BB%83'
'%E4%B8%AD%E4%BD%91%2B9030.png'),
),
),
ReorderableSliverList(
delegate: ReorderableSliverChildListDelegate(_rows),
// or use ReorderableSliverChildBuilderDelegate if needed
// delegate: ReorderableSliverChildBuilderDelegate(
// (BuildContext context, int index) => _rows[index],
// childCount: _rows.length
// ),
onReorder: _onReorder,
)
],
);
}
}
ReorderableSliverList Demo

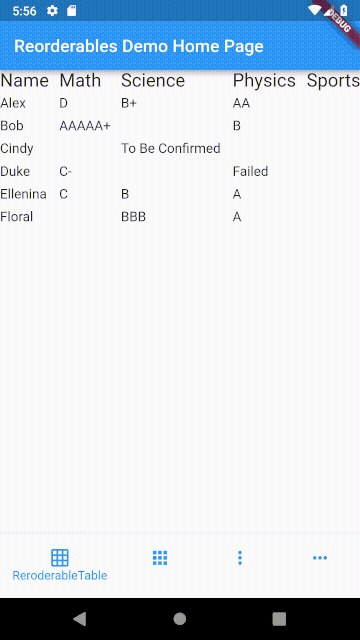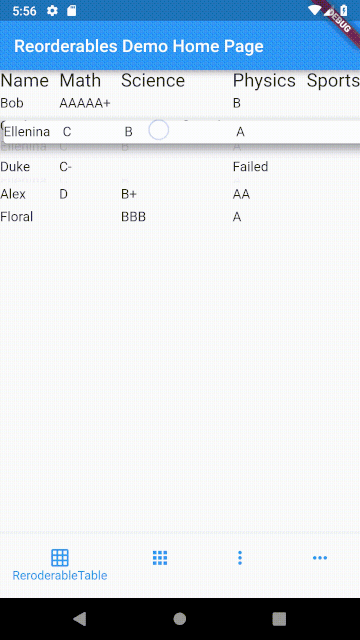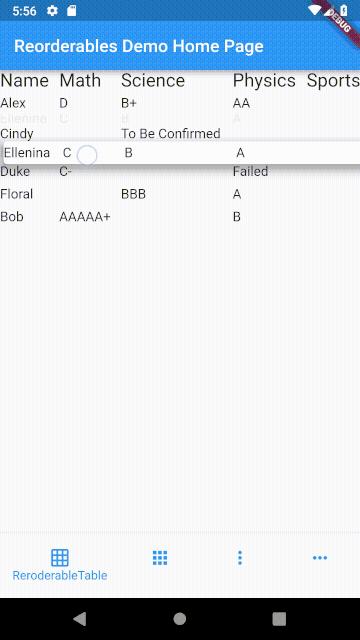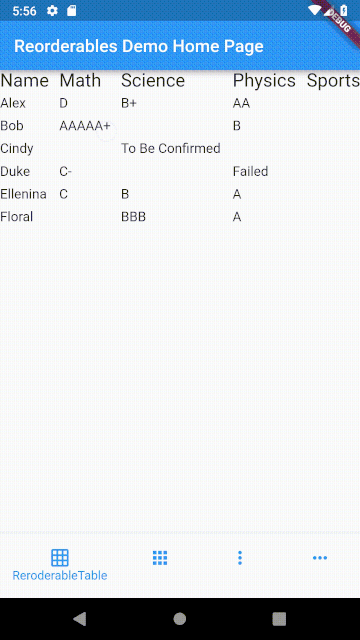
ReorderableTable #
The difference between table and list is that cells in a table are horizontally aligned, whereas in a list, each item can have children but they are not aligned with children in another item.
Making a row draggable requires cells to be contained in a single widget. This isn't achievable with Table or GridView widget since their children are laid out as cells of widget instead of rows of widget.
class _TableExampleState extends State<TableExample> {
List<ReorderableTableRow> _itemRows;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
var data = [
['Alex', 'D', 'B+', 'AA', ''],
['Bob', 'AAAAA+', '', 'B', ''],
['Cindy', '', 'To Be Confirmed', '', ''],
['Duke', 'C-', '', 'Failed', ''],
['Ellenina', 'C', 'B', 'A', 'A'],
['Floral', '', 'BBB', 'A', 'A'],
];
Widget _textWithPadding(String text) {
return Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 4),
child: Text(text, textScaleFactor: 1.1),
);
}
_itemRows = data.map((row) {
return ReorderableTableRow(
//a key must be specified for each row
key: ObjectKey(row),
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.max,
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: <Widget>[
_textWithPadding('${row[0]}'),
_textWithPadding('${row[1]}'),
_textWithPadding('${row[2]}'),
_textWithPadding('${row[3]}'),
// Text('${row[4]}'),
],
);
}).toList();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
var headerRow = ReorderableTableRow(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.max,
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: [
Text('Name', textScaleFactor: 1.5),
Text('Math', textScaleFactor: 1.5),
Text('Science', textScaleFactor: 1.5),
Text('Physics', textScaleFactor: 1.5),
Text('Sports', textScaleFactor: 1.5)
]
);
void _onReorder(int oldIndex, int newIndex) {
setState(() {
ReorderableTableRow row = _itemRows.removeAt(oldIndex);
_itemRows.insert(newIndex, row);
});
}
return ReorderableTable(
header: headerRow,
children: _itemRows,
onReorder: _onReorder,
);
}
}
In a table, cells in each row are aligned on column basis with cells in other rows, whereas cells in a row of a list view don't align with other rows.
ReorderableTable Demo

ReorderableWrap #
This widget can also limit the minimum and maximum amount of children in each run, on top of the size-based policy in Wrap's algorithm. See API references for more details.
class _WrapExampleState extends State<WrapExample> {
final double _iconSize = 90;
List<Widget> _tiles;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_tiles = <Widget>[
Icon(Icons.filter_1, key: ValueKey(1), size: _iconSize),
Icon(Icons.filter_2, key: ValueKey(2), size: _iconSize),
Icon(Icons.filter_3, key: ValueKey(3), size: _iconSize),
Icon(Icons.filter_4, key: ValueKey(4), size: _iconSize),
Icon(Icons.filter_5, key: ValueKey(5), size: _iconSize),
Icon(Icons.filter_6, key: ValueKey(6), size: _iconSize),
Icon(Icons.filter_7, key: ValueKey(7), size: _iconSize),
Icon(Icons.filter_8, key: ValueKey(8), size: _iconSize),
Icon(Icons.filter_9, key: ValueKey(9), size: _iconSize),
];
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
void _onReorder(int oldIndex, int newIndex) {
setState(() {
Widget row = _tiles.removeAt(oldIndex);
_tiles.insert(newIndex, row);
});
}
return ReorderableWrap(
spacing: 8.0,
runSpacing: 4.0,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
children: _tiles,
onReorder: _onReorder
);
}
}
ReorderableWrap Demo

ReorderableColumn example #1 #
class _ColumnExample1State extends State<ColumnExample1> {
List<Widget> _rows;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_rows = List<Widget>.generate(50,
(int index) => Text('This is row $index', key: ValueKey(index), textScaleFactor: 1.5)
);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
void _onReorder(int oldIndex, int newIndex) {
setState(() {
Widget row = _rows.removeAt(oldIndex);
_rows.insert(newIndex, row);
});
}
return ReorderableColumn(
header: Text('THIS IS THE HEADER ROW'),
footer: Text('THIS IS THE FOOTER ROW'),
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: _rows,
onReorder: _onReorder,
);
}
}
ReorderableColumn example #1 Demo

ReorderableColumn example #2 #
class _ColumnExample2State extends State<ColumnExample2> {
List<Widget> _rows;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_rows = List<Widget>.generate(10,
(int index) => Text('This is row $index', key: ValueKey(index), textScaleFactor: 1.5)
);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
void _onReorder(int oldIndex, int newIndex) {
setState(() {
Widget row = _rows.removeAt(oldIndex);
_rows.insert(newIndex, row);
});
}
Widget reorderableColumn = IntrinsicWidth(
child: ReorderableColumn(
header: Text('List-like view but supports IntrinsicWidth'),
// crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: _rows,
onReorder: _onReorder,
)
);
return Transform(
transform: Matrix4.rotationZ(0),
alignment: FractionalOffset.topLeft,
child: Material(
child: Card(child: reorderableColumn),
elevation: 6.0,
color: Colors.transparent,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.zero,
),
);
}
}
ReorderableColumn example #2 Demo

ReorderableRow #
See exmaple/lib/row_example.dart
ReorderableRow Demo

Support #
If you like my work, you can support me by buying me a coffee or donate me via PayPal. Your support is very much appreciated. :)





