supabase_flutter 2.3.1  supabase_flutter: ^2.3.1 copied to clipboard
supabase_flutter: ^2.3.1 copied to clipboard
Flutter integration for Supabase. This package makes it simple for developers to build secure and scalable products.
supabase_flutter #
Flutter Client library for Supabase.
- Documentation: https://supabase.com/docs/reference/dart/introduction
Platform Support #
Except Linux, all platforms are fully supported. Linux only doesn't support deeplinks, because of our dependency app_links. All other features are supported.
Getting Started #
Import the package:
import 'package:supabase_flutter/supabase_flutter.dart';
Initialize Supabase before using it:
import 'package:supabase_flutter/supabase_flutter.dart';
void main() async {
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
await Supabase.initialize(
url: SUPABASE_URL,
anonKey: SUPABASE_ANON_KEY,
);
runApp(MyApp());
}
// It's handy to then extract the Supabase client in a variable for later uses
final supabase = Supabase.instance.client;
Usage example #
Authentication #
final supabase = Supabase.instance.client;
// Email and password sign up
await supabase.auth.signUp(
email: email,
password: password,
);
// Email and password login
await supabase.auth.signInWithPassword(
email: email,
password: password,
);
// Magic link login
await supabase.auth.signInWithOtp(email: 'my_email@example.com');
// Listen to auth state changes
supabase.auth.onAuthStateChange.listen((data) {
final AuthChangeEvent event = data.event;
final Session? session = data.session;
// Do something when there is an auth event
});
Native Apple Sign in
You can perform Apple sign in using the sign_in_with_apple package on Flutter.
Follow the instructions on README of the sign_in_with_apple package to setup the native Apple sign in on iOS and macOS.
Once the setup is complete on the Flutter app, add the bundle ID of your app to your Supabase dashboard in Authentication -> Providers -> Apple in order to register your app with Supabase.
import 'package:sign_in_with_apple/sign_in_with_apple.dart';
import 'package:supabase_flutter/supabase_flutter.dart';
/// Performs Apple sign in on iOS or macOS
Future<AuthResponse> signInWithApple() async {
final rawNonce = supabase.auth.generateRawNonce();
final hashedNonce = sha256.convert(utf8.encode(rawNonce)).toString();
final credential = await SignInWithApple.getAppleIDCredential(
scopes: [
AppleIDAuthorizationScopes.email,
AppleIDAuthorizationScopes.fullName,
],
nonce: hashedNonce,
);
final idToken = credential.identityToken;
if (idToken == null) {
throw const AuthException(
'Could not find ID Token from generated credential.');
}
return signInWithIdToken(
provider: OAuthProvider.apple,
idToken: idToken,
nonce: rawNonce,
);
}
Native Google sign in
You can perform native Google sign in on Android and iOS using google_sign_in. For platform specific settings, follow the instructions on README of the package.
First, create client IDs for your app. You need to create a web client ID as well to perform Google sign-in with Supabase.
Once you have registered your app and created the client IDs, add the web client ID in your Supabase dashboard in Authentication -> Providers -> Google. Also turn on the Skip nonce check option, which will enable Google sign-in on iOS.
At this point you can perform native Google sign in using the following code. Be sure to replace the webClientId and iosClientId with your own.
import 'package:google_sign_in/google_sign_in.dart';
import 'package:supabase_flutter/supabase_flutter.dart';
...
Future<AuthResponse> _googleSignIn() async {
/// TODO: update the Web client ID with your own.
///
/// Web Client ID that you registered with Google Cloud.
const webClientId = 'my-web.apps.googleusercontent.com';
/// TODO: update the iOS client ID with your own.
///
/// iOS Client ID that you registered with Google Cloud.
const iosClientId = 'my-ios.apps.googleusercontent.com';
// Google sign in on Android will work without providing the Android
// Client ID registered on Google Cloud.
final GoogleSignIn googleSignIn = GoogleSignIn(
clientId: iosClientId,
serverClientId: webClientId,
);
final googleUser = await googleSignIn.signIn();
final googleAuth = await googleUser!.authentication;
final accessToken = googleAuth.accessToken;
final idToken = googleAuth.idToken;
if (accessToken == null) {
throw 'No Access Token found.';
}
if (idToken == null) {
throw 'No ID Token found.';
}
return supabase.auth.signInWithIdToken(
provider: OAuthProvider.google,
idToken: idToken,
accessToken: accessToken,
);
}
...
OAuth login #
For providers other than Apple or Google, you need to use the signInWithOAuth() method to perform OAuth login. This will open the web browser to perform the OAuth login.
Use the redirectTo parameter to redirect the user to a deep link to bring the user back to the app. Learn more about setting up deep links in Deep link config.
// Perform web based OAuth login
await supabase.auth.signInWithOAuth(
OAuthProvider.github,
redirectTo: kIsWeb ? null : 'io.supabase.flutter://callback',
);
// Listen to auth state changes in order to detect when ther OAuth login is complete.
supabase.auth.onAuthStateChange.listen((data) {
final AuthChangeEvent event = data.event;
if(event == AuthChangeEvent.signedIn) {
// Do something when user sign in
}
});
Database #
Database methods are used to perform basic CRUD operations using the Supabase REST API. Full list of supported operators can be found here.
// Select data with filters
final data = await supabase
.from('cities')
.select()
.eq('country_id', 1) // equals filter
.neq('name', 'The shire'); // does not equal filter
// Insert a new row
await supabase
.from('cities')
.insert({'name': 'The Shire', 'country_id': 554});
Realtime #
Realtime data as Stream
To receive realtime updates, you have to first enable Realtime on from your Supabase console. You can read more here on how to enable it.
Warning When using
stream()with aStreamBuilder, make sure to persist the stream value as a variable in aStatefulWidgetinstead of directly constructing the stream within your widget tree, which could cause rapid rebuilds that will lead to losing realtime connection.
class MyWidget extends StatefulWidget {
const MyWidget({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
State<MyWidget> createState() => _MyWidgetState();
}
class _MyWidgetState extends State<MyWidget> {
// Persisting the future as local variable to prevent refetching upon rebuilds.
final stream = supabase.from('countries').stream(primaryKey: ['id']);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return StreamBuilder<List<Map<String, dynamic>>>(
stream: stream,
builder: (context, snapshot) {
// return your widget with the data from snapshot
},
);
}
}
Postgres Changes
You can get notified whenever there is a change in your Supabase tables.
final myChannel = supabase.channel('my_channel');
myChannel
.onPostgresChanges(
event: PostgresChangeEvent.all,
schema: 'public',
table: 'countries',
callback: (payload) {
// Do something fun or interesting when there is an change on the database
},
)
.subscribe();
Broadcast
Broadcast lets you send and receive low latency messages between connected clients by bypassing the database.
final myChannel = supabase.channel('my_channel');
// Subscribe to `cursor-pos` broadcast event
final myChannel = supabase.channel('my_channel');
myChannel
.onBroadcast(event: 'cursor-pos', callback: (payload) {}
// Do something fun or interesting when there is an change on the database
)
.subscribe();
// Send a broadcast message to other connected clients
await myChannel.sendBroadcastMessage(
event: 'cursor-pos',
payload: {'x': 30, 'y': 50},
);
Presence #
Presence let's you easily create "I'm online" feature.
final myChannel = supabase.channel('my_channel');
// Subscribe to presence events
myChannel
.onPresence(
event: PresenceEvent.sync,
callback: (payload) {
final onlineUsers = myChannel.presenceState();
// handle sync event
})
.onPresence(
event: PresenceEvent.join,
callback: (payload) {
// New users have joined
})
.onPresence(
event: PresenceEvent.leave,
callback: (payload) {
// Users have left
})
.subscribe(((status, [_]) async {
if (status == RealtimeSubscribeStatus.subscribed) {
// Send the current user's state upon subscribing
final status = await myChannel
.track({'online_at': DateTime.now().toIso8601String()});
}
}));
Storage #
final file = File('example.txt');
file.writeAsStringSync('File content');
await supabase.storage
.from('my_bucket')
.upload('my/path/to/files/example.txt', file);
// Use the `uploadBinary` method to upload files on Flutter web
await supabase.storage
.from('my_bucket')
.uploadBinary('my/path/to/files/example.txt', file.readAsBytesSync());
Edge Functions #
final data = await supabase.functions.invoke('get_countries');
Deep links #
Why do you need to setup deep links #
You need to setup deep links if you want your native app to open when a user clicks on a link. User clicking on a link and the app opens up happens in a few scenarios when you use Supabase auth, and in order to support those scenarios, you need to setup deep links.
When do you need to setup deep links #
- Magic link login
- Have
confirm emailenabled and are using email login - Resetting password for email login
- Calling
.signInWithOAuth()method
*Currently supabase_flutter supports deep links on Android, iOS, Web, MacOS and Windows.
Dashboard Deep link config #
- Go to your Supabase project Authentication Settings page.
- You need to enter your app redirect callback on
Additional Redirect URLsfield.
The redirect callback url should have this format [YOUR_SCHEME]://[YOUR_HOSTNAME]. Here, io.supabase.flutterdemo://login-callback is just an example, you can choose whatever you would like for YOUR_SCHEME and YOUR_HOSTNAME as long as the scheme is unique across the user's device. For this reason, typically a reverse domain of your website is used.
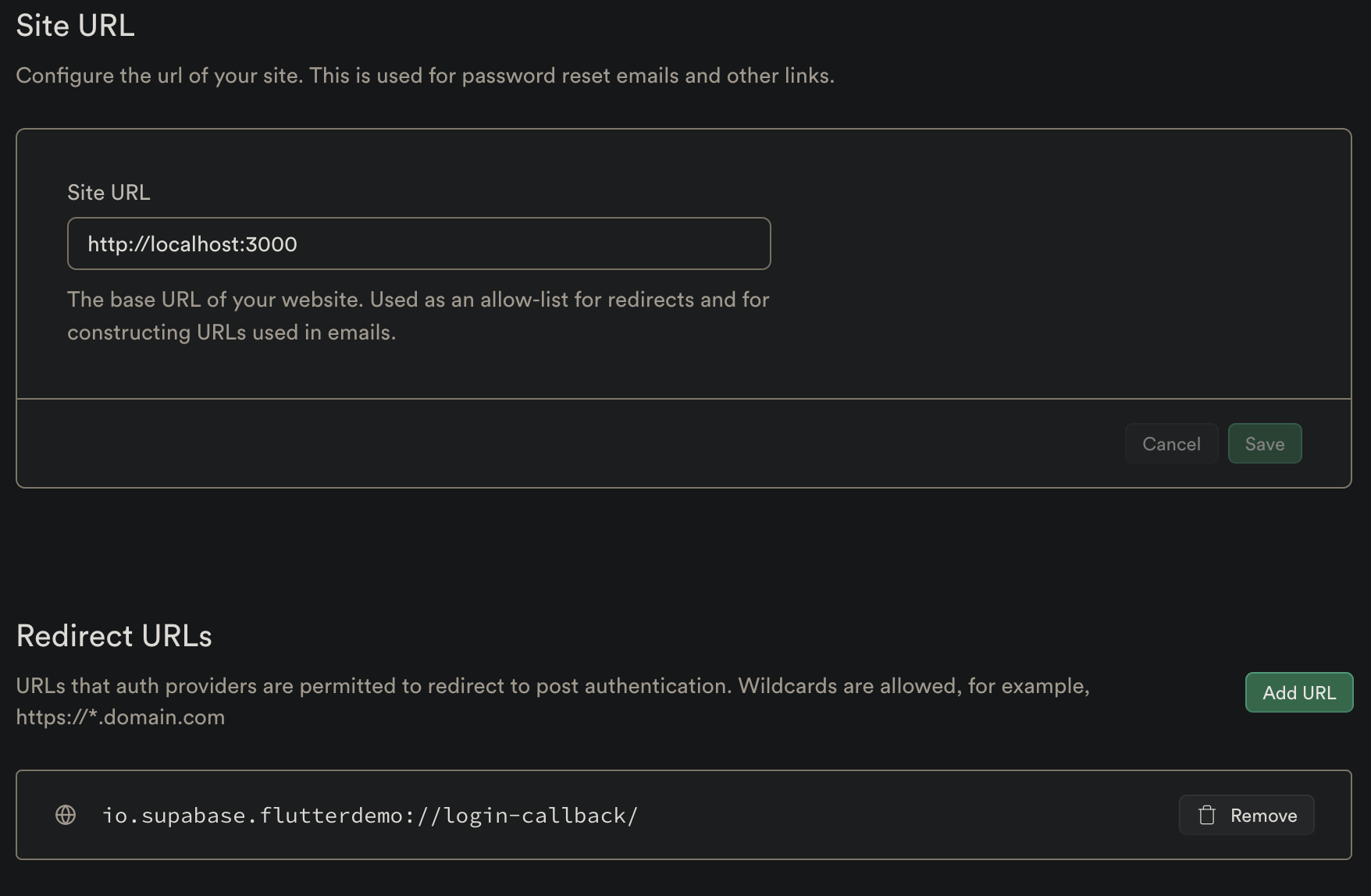
Flutter Deep link config #
supabase_flutter uses app_link internally to handle deep links. You can find the platform specific config to setup deep links in the following.
https://github.com/llfbandit/app_links/tree/master?tab=readme-ov-file#getting-started
Platform specific config #
Follow the guide to find additional platform specidic condigs for your OAuth provider.
https://supabase.io/docs/guides/auth#third-party-logins
Custom LocalStorage #
As default, supabase_flutter uses Shared preferences to persist the user session.
However, you can use any other methods by creating a LocalStorage implementation. For example, we can use flutter_secure_storage plugin to store the user session in a secure storage.
// Define the custom LocalStorage implementation
class MockLocalStorage extends LocalStorage {
final storage = FlutterSecureStorage();
@override
Future<void> initialize() async {}
@override
Future<String?> accessToken() async {
return storage.containsKey(key: supabasePersistSessionKey);
}
@override
Future<bool> hasAccessToken() async {
return storage.read(key: supabasePersistSessionKey);
}
@override
Future<void> persistSession(String persistSessionString) async {
return storage.write(key: supabasePersistSessionKey, value: persistSessionString);
}
@override
Future<void> removePersistedSession() async {
return storage.delete(key: supabasePersistSessionKey);
}
}
// use it when initializing
Supabase.initialize(
...
authOptions: FlutterAuthClientOptions(
localStorage: const EmptyLocalStorage(),
),
);
You can also use EmptyLocalStorage to disable session persistence:
Supabase.initialize(
// ...
authOptions: FlutterAuthClientOptions(
localStorage: const EmptyLocalStorage(),
),
);
Contributing #
- Fork the repo on GitHub
- Clone the project to your own machine
- Commit changes to your own branch
- Push your work back up to your fork
- Submit a Pull request so that we can review your changes and merge
License #
This repo is licenced under MIT.
